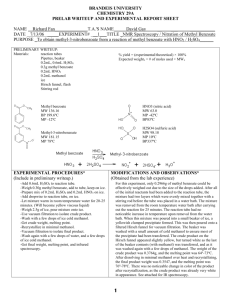
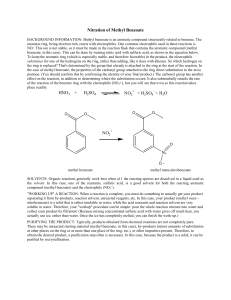
Sub-headings formatted as Level 2: use 12 point Helvetica
advertisement

Proceedings of the NARST 2009 Annual Meeting (Assuming there are five levels of headings, the title should be formatted as level 5 using 12 point Helvetica– ALL CAPS and centered, see 5th edition of the APA Publication Manual, p. 113) ATMOSPHERIC COMPOUND IS DOUBLE-EDGED SWORD IN CLIMATE CHANGE (Abstract formatted as block text – 12 point Times New Roman, 0.5” left and right indents). Recent studies suggest that an atmospheric compound derived primarily from coal combustion may have contradictory effects on the earth's climate. (For authors, use body text, with left justification, as shown below) Author 1, Institution (body text – 12 point Times New Roman) Author 2, Institution (body text – 12 point Times New Roman) Author 3, Institution (body text – 12 point Times New Roman) (Next heading should be formatted as Level 1 – using 12 point Helvetica, using Uppercase and Lowercase Heading) Sulphuric Acid: The Key Reactant (The text should be in Normal at 12 point, Times New Roman) Under many conditions, sulfuric acid may cool the earth's atmosphere. Sulfuric acid particles seem to scatter ultraviolet light back into space before it has a change to enter the troposphere - the bottom layer of earth's atmosphere. But if conditions are right, this same chemical can warm the earth by combining with other compounds in the atmosphere to form clouds. Researchers looked at the interaction of sulfuric acid and methanol and what the compounds' combined effect might mean to global climate change. Both compounds are usually found in aerosol form in the upper atmosphere. Scientists believe that methanol comes primarily from natural sources, such as oceans, forests and the decay of organic matter. While there are a few natural sources for sulfuric acid, such as volcanoes and marine sea spray, its precursor - sulfur dioxide - comes mainly from the burning of coal. In the atmosphere, sulfur dioxide is oxidized primarily by atmospheric moisture, resulting in sulfuric acid. (Sub-headings formatted as Level 2: use 12 point Helvetica – Centered and Italicized, with Upper Case and Lowercase Heading) Role of Sulphuric Acid What the researchers discovered is that sulfuric acid molecules in atmospheric aerosols can act as sort of a force field by reflecting light and heat back into space, said one scientist. This reflection contributes to a cooling effect on the earth. Methanol by itself doesn't really have an effect on climate change. (For level 3, use Flush Left, Italicised, Upper case and Lowercase Side Heading) Reactions of Sulfuric Acid When the two molecules get together (about 5 to 10 percent of the methanol in the atmospheric aerosols reacts with sulfuric acid) they form methyl sulfate. Methyl sulfate is less volatile than methanol, meaning there's less chance that methyl sulfate will evaporate or be vaporized. And while it seems like a relatively small amount of methanol gets converted to methyl sulfate, it is still enough to have an impact on global climate change, say some researchers. (Level 4: Indented, italicized, lowercase paragraph heading ending with a period.) Details on Reactions of Sulfuric Acid and Methanol The scientists found that methyl sulfate's stability provides a springboard for cloud formation - water droplets collect on the stable molecules and eventually form clouds. Instead of causing light and heat to bounce back into space, most clouds create a warming effect by trapping light and heat in the atmosphere. (Quotations, see 5th edition APA Publication Manual, pp. 117-122, for quotes of fewer than 40 words, incorporate into the paragraph using Normal. With quotes 40 or more words, indent 0.5” on the left, using Block text.) See examples below: One scientist said, "Right now these aerosols are probably helping to slow down the human-induced warming effect on the earth, but it's a complicated balance that we're struggling to fully understand.” She added: More aerosols emitted into the atmosphere may lead to cooling. However, if these aerosols were able to combine with other compounds and ultimately form clouds, it could have a warming effect. There's a complex balance between warming and cooling in the atmosphere. For tables (pp. 147-176) and figures (pp. 176-201), please refer to sections in 5th edition of the APA Publication Manual. PLEASE SUBMIT ALL PROCEEDINGS DOCUMENTS AS A PDF FILE TO INFO@NARST.ORG BY DEADLINE OF March 15, 2009. 2