Acid-Base Balance & Buffers: Lecture Notes
advertisement

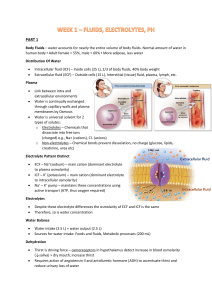
Acid-Base Balance and Buffers Buffer: a system consisting of a weak acid and a weak base designed to prevent large shifts in pH which could be harmful or potentially fatal to the body Recall: acids tend to give up H+ ions bases tend to accept H+ ions In the body a common buffer system uses Carbonic acid H2CO3 and Bicarbonate HCO3When CO2 dissolves in our blood plasma we get carbonic acid: CO2 + H2O H2CO3 HCO3- + H+ This can result in excess H+ ions, depending on CO2 levels. Our kidneys regulate the amount of bicarbonate in the body and have excess HCO3- available to “mop up” the extra H+ ions. This prevents wild pH shifts. Excess H+ ions in the blood will trigger increased respiration to reduce the acidity and increase the pH of the blood. If CO2 levels are too low, as in hyperventilation, then bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) don’t have many H+ ions to bind. The kidneys will eliminate excess HCO3- in the urine.