Homeostasis - 7.5 7.6
advertisement

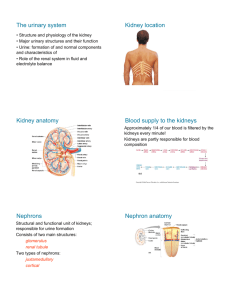
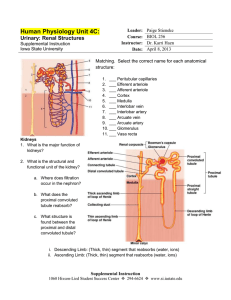
Formation of Urine & Water Balance 7.5, 7.6 First, some review… What is this? quizlet.com • Remember this website? http://quizlet.com/1644286/homeostasisterms-flash-cards/ • this is a set of Homeostasis flashcards How is urine formed? Urine Formation (Image on previous slide from: http://www.mountainside-medical.com/products/Urine-Specimen-Cup,-Sterile.html) • filtration • reabsorption • secretion Filtration • glomerulus high pressure: 65mm Hg • smaller dissolved molecules can move through the walls of the glomerulus • 600mL of blood flows through the kidneys each minute; 120mL is filtered Reabsorption • 119mL of every 120mL of glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed (phew!) • 3 main substances reabsorbed: – water (passive) – all glucose (active) – Na+ (active) • also amino acids (active), Cl- and HCO3(charge attraction), etc. Secretion • nitrogen-containing wastes (such as NH3, urea, uric acid), H+ ions, and K+ ions are secreted in the distal tubule • Simple animation on urine formation with no narration: • http://www.kidneypatientguide.org.uk/site/HKWanim.php Review • This interactive animation has a nice feature where you can track the movement of various substances: • http://www.biologymad.com/resources/kidney.swf • Narrated animation on urine formation: • http://davisplus.fadavis.com/scanlon6e/Animations/animations.cfm?exe rcise=NephronFiltration&title=Nephron%20Filtration • Narrated animation of structure & function; quite detailed: • http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp51/51020.html 7.6 - Water Balance Water Balance (Image on next slide from: http://knight.noble-hs.sad60.k12.me.us/content/exploringLife/text/chapter32/concept32.2.html) • water balance (i.e. amount of water in the blood) is regulated by the hypothalamus • osmoreceptors detect changes in blood solute concentration • release of ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) increases water reabsorption Blood Pressure Regulation • blood pressure receptors in the juxtaglomerular apparatus release renin, which activates angiotensinogen • angiotensin causes the adrenal glands to release aldosterone • aldosterone is a hormone that acts on nephrons to increase Na+ reabsorption in the distal tubule and collecting duct (Image from: http://www.colorado.edu/intphys/Class/IPHY3430-200/017kidneys.htm) pH balance • cellular respiration produces CO2 as a waste product • CO2 dissolved in the blood becomes H2CO3 (carbonic acid) • carbonic acid dissociates into H+ (acidic) and HCO3- (basic) pH balance pH balance • peritubular capillaries actively transport CO2 to the tubules • generates H+ and HCO3- ions • HCO3- ions diffuse back into blood • H+ ions combine with phosphate ions or ammonia and are removed by the kidneys Images in Slides #3,4,5 Excretory system: • http://faculty.ccri.edu/kamontgomery/anatomy%20lab_13%20uro genital.htm Kidney: • http://www.dorenarode.com/anatomy/openlab.htm Nephron (colour): • http://movies-ciarancolegage.blogspot.com/2011/03/kidneydiagram-labeled.html Nephron (unlabelled): • http://kenpitts.net/hbio/46skel_musc_integ_systems/ch46_sched _08.htm