Homwork #9&10
advertisement
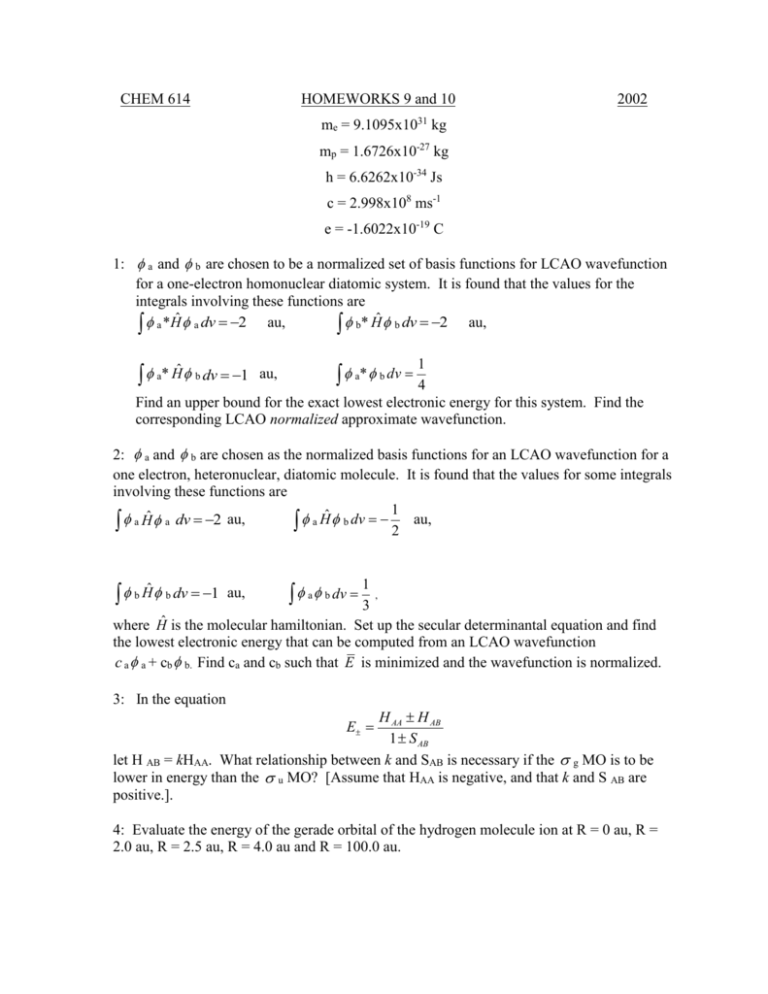
CHEM 614 HOMEWORKS 9 and 10 2002 me = 9.1095x1031 kg mp = 1.6726x10-27 kg h = 6.6262x10-34 Js c = 2.998x108 ms-1 e = -1.6022x10-19 C 1: a and b are chosen to be a normalized set of basis functions for LCAO wavefunction for a one-electron homonuclear diatomic system. It is found that the values for the integrals involving these functions are a *Hˆ a dv 2 au, b* Ĥ b dv 2 au, a* Ĥ b dv 1 au, 1 a* b dv 4 Find an upper bound for the exact lowest electronic energy for this system. Find the corresponding LCAO normalized approximate wavefunction. 2: a and b are chosen as the normalized basis functions for an LCAO wavefunction for a one electron, heteronuclear, diatomic molecule. It is found that the values for some integrals involving these functions are 1 a Ĥ a dv 2 au, a Ĥ b dv 2 au, b Ĥ b dv 1 au, 1 a b dv 3 , where Ĥ is the molecular hamiltonian. Set up the secular determinantal equation and find the lowest electronic energy that can be computed from an LCAO wavefunction c a a + cb b. Find ca and cb such that E is minimized and the wavefunction is normalized. 3: In the equation H AA H AB 1 S AB let H AB = kHAA. What relationship between k and SAB is necessary if the g MO is to be lower in energy than the u MO? [Assume that HAA is negative, and that k and S AB are positive.]. E 4: Evaluate the energy of the gerade orbital of the hydrogen molecule ion at R = 0 au, R = 2.0 au, R = 2.5 au, R = 4.0 au and R = 100.0 au. 5: For a homonuclear diatomic molecule aligned with the inter-nuclear direction as the defined z-axis, characterize each of the following MO's as , , , and g or u, and bonding or antibonding. a) 2pya + 2pyb b) 2pza + 2pzb c) 3dz2a + 3dz2b d) 3dxya + 3dxyb e) 3dxza - 3dxzb 6: Indicate whether you expect each of the following homonuclear diatomic MO's to be bonding or antibonding. Sketch the MO in each case: a) u b) u c) g 7: A homonuclear diatomic molecule MO of u symmetry is to be expressed as a linear combination of AOs centered on the nuclei, which lie on the z axis. Which of the AOs in the following list can contribute to the MO? 1s 2s 2px 2py 2pz 3s 3px 3py 3pz 3dxy 3dxz 3dyz 3dz2 3dx2-y2 8: Use the sketches and symmetry arguments to decide which of the following integrals vanish for diatomic molecules (the z axis is the inter-nuclear one): (a) 2 p za1sb dv, (b) 2 p ya1sb dv, (c) 2 p za2pyb dv, (d) 2 p ya3dyzb dv (e) 2 p za3dyzb dv 9: Assuming the inter-nuclear axis to lie along the z coordinate, what are the possible ML quantum numbers for an MO constructed from 3dz2a - 3dz2b? 10: a) write out the ground state configuration for O2 and O2+ using MO symmetry symbols (1 g2, etc.) b) What is the net number of bonding electrons in both molecules? c) What is the bond order of both species? d) How does the dissociation energy for O2+ compare to that for O2? e) What spin multiplicity would you expect for the two ground states? f) In O2+, which occupied MO's may contain contributions from 2pz AO's, assuming z is the inter-nuclear axis?