Chemical Equations
advertisement

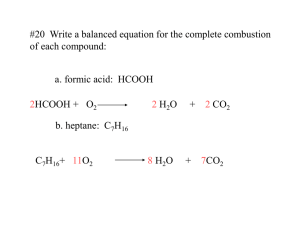
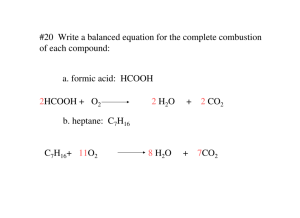
Chemical Reactions (1) Composition Reactions (also known as combination reactions or synthesis reactions) – In a composition reaction, two or more reactants combine to form one product. General Pattern: A + B AB A and B are elements or compounds; AB is a compound Balance the following composition equations: Mg + O2 MgO C + O2 CO2 K + S K2S (2) Decomposition Reactions – In a decomposition reaction a substance is broken down into two or more simpler substances. General Pattern: AB A + B AB is a compound; A and B are compounds or elements Balance the following decomposition equations: HgO Ag2O Ca(OH)2 Fe2(SO4)3 Hg + O2 Ag + O2 CaO + H2O Fe2O3 + SO3 Special Decomposition Reactions (i) Decomposition of a chlorate compounds yields a chloride compound plus oxygen gas: Ex. 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 (ii) Decomposition of a nitrate compound yields a nitrite compound plus oxygen gas: Ex. 2KNO3 2KNO2 + O2 (iii) Decomposition of a carbonate compound yields an oxide compound plus carbon dioxide: Ex. K2CO3 K2O + CO2 Write the balanced equation for the decomposition of: (a) sodium chlorate (b) magnesium nitrate (c) calcium carbonate (3) Single displacement or single replacement reactions – In this type of reaction, one element displaces another in a compound. This happens in two situations: General Pattern: A + BC AC + B if A is a metal Or: A + BC BA + C if A is a non-metal (i) When a metal displaces a metal Ex. Li + NaCl LiCl + Na (ii) When a non-metal displaces a non-metal Ex. F2 + 2KI I2 + 2KF Write the equation for copper reacting with silver nitrate (assume copper (II)): Write the equation for lithium reacting with hydrogen hydroxide (4) Double displacement or double replacement reactions – In a double replacement reaction, two ionic compounds switch cations General Pattern: AB + CD AD + CB Example: (NH4)2S + FeSO4 FeS + (NH4)2SO4 Na2CO3 (aq) + 2HCl 2NaCl (aq) + H2CO3 (aq) This decomposes to give H2O + CO2 (5) Hydrocarbon burning or combustion reaction – Almost all organic compounds will burn in air. When an organic compound burns in air, it is reacting with the oxygen in the air. The products under normal conditions are carbon dioxide and water. This is called complete combustion. Balance the following complete combustion equations: CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O C4H10 + O2 CO2 + H2O C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O If incomplete combustion takes place, the products are carbon monoxide and water. Balance the following incomplete combustion equation: C3H8 + O2 CO + H2O CH4 + O2 CO + H2O