6.1-6.2 Synthesis, decompositon and combustion reactions
advertisement

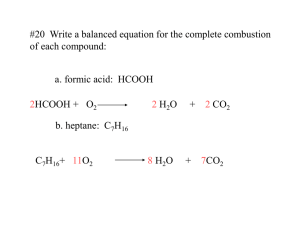
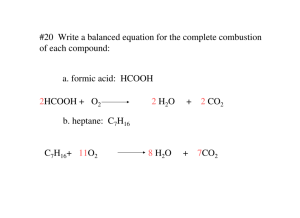
6.1-6.2 Reaction Types Synthesis, Decomposition and Combustion Types of Chemical Reactions There are 6 ways elements and compounds may interact You can predict the products of a reaction if you can identify the reactants you are using General chemical equations (GCE) use letters in the place of the symbols of elements. They help you identify the reaction type Symbols in GCE A single letter is a metal or non-metal Ex. A, B, X H is for the hydrogen in an acid OH is for hydroxide in a base Two letters Ex. AB, CD represent a compound Example: GCE: HB + XOH XB + H2O Word equation: sulfuric acid + sodium hydroxide sodium sulfate + water Skeleton equation: H2SO4 (aq) + NaOH (s) Na2SO4 (aq) + H2O (l) Balanced Equation: H2SO4 (aq) + 2 NaOH (s) Na2SO4 (aq) + 2 H2O (l) 1. Synthesis Reactions Element + Element Compound In general A + B AB Example: Mg (s) + O2 (g) MgO (s) S8 (g) + O2(g) SO2 (g) H2 (g) + N2 (g) 2NH3 (g) 2. Decomposition Reactions A compound is broken down into two or more elements or simpler compounds Compound Element + Element In general, AB A + B Example: 2 HgO (s) 2 Hg (l) + O2(g) 2 H2O (l) 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g) 3.Combustion Reactions A compound or element rapidly reacts with oxygen gas Heat and light are given off Usually involve a hydrocarbon (a compound made up of only hydrogen and carbon) The formula for a hydrocarbon is general CxHy (x and y are subscript numbers) Ex. CH4 is methane Combustion A. Complete combustion -plenty of oxygen is available In general, CxHy (g)+ O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O (l) Incomplete combustion -Oxygen is in limited supply B. In general, CxHy (g)+ O2 (g) C(s) + CO (g) + CO2 (g) + H2O (l) Impact on the Environment Global warming – the combustion of hydrocarbons releases carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas Cleaning oil spills – on land, the oil can be set on fire (combustion) then the contaminated soil is removed for additional treatment Determine the reaction type 2 Na + Cl2 2 NaCl Type: CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O Type: 2NI3 N2 + 3 I2 Type: Predict the Products 1. 2. 3. NH3 Na + Cl2 S8 + O2 Type:_______ Type:_______ Type:_______ plenty 4. CH4 + O2 Type:_______ deficient 5. C 2H 6 + O2 Type:_______ Homework p. 229 #4-10