6.5 Types of Chemical Reactionsfill
advertisement
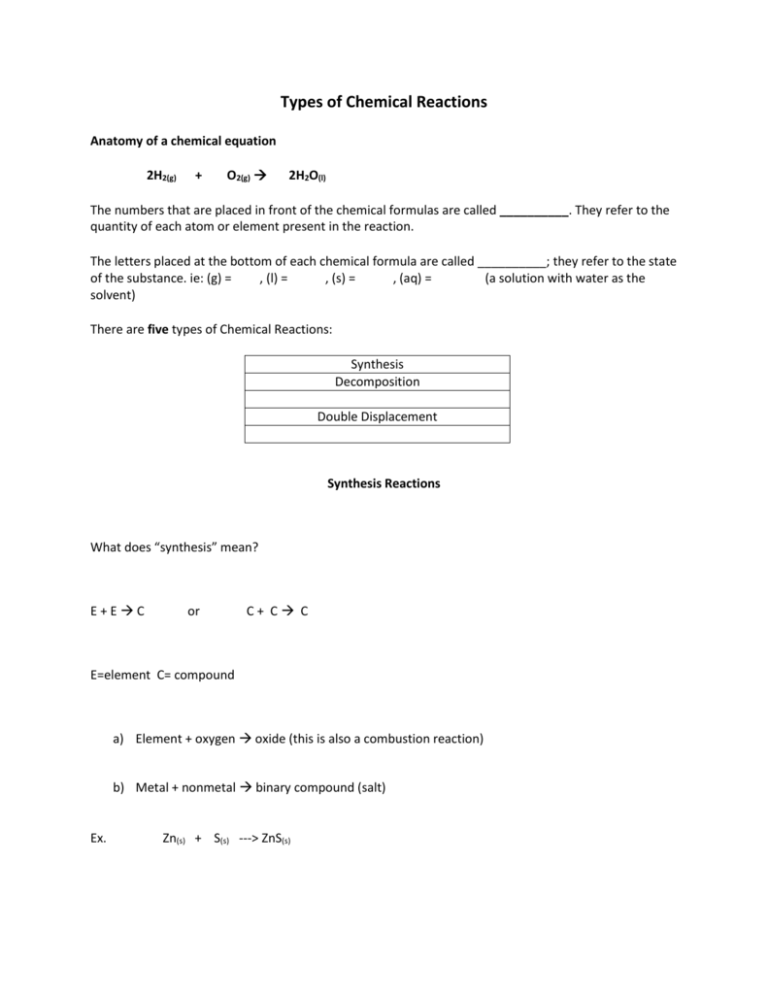
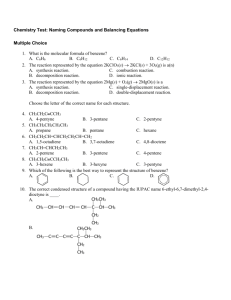
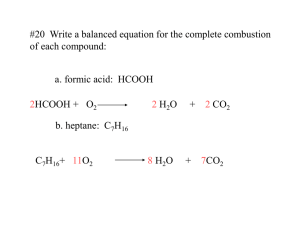
Types of Chemical Reactions Anatomy of a chemical equation 2H2(g) + O2(g) 2H2O(l) The numbers that are placed in front of the chemical formulas are called __________. They refer to the quantity of each atom or element present in the reaction. The letters placed at the bottom of each chemical formula are called __________; they refer to the state of the substance. ie: (g) = , (l) = , (s) = , (aq) = (a solution with water as the solvent) There are five types of Chemical Reactions: Synthesis Decomposition Double Displacement Synthesis Reactions What does “synthesis” mean? E+EC or C+ C C E=element C= compound a) Element + oxygen oxide (this is also a combustion reaction) b) Metal + nonmetal binary compound (salt) Ex. Zn(s) + S(s) ---> ZnS(s) Na(s) + Cl2(g) ----> NH3(g) + HCl(g) -----> NaCl(s) NH4Cl(s) Decomposition Reactions What does decomposition mean? CE+E or C C+E The types are the same as the synthesis reactions but reversed. Let’s try some examples: ex. Energy + H2O (l) ---> H2 (g) + ex. Na3N(s) ex. CaCO3(s) ----> CO2(g) + CaO(s) -----> Na(s) + N2(g) O2(g) Single Displacement Reactions A + BC AC + B or AB + C AC + B In these reactions, a metal element replaces metal in a compound, or non-metal element replaces nonmetal in a compound. **Reminder Cation: positive ion, Anion: negative ion ex. sodium + silver fluoride ------> silver ex. Cu + CuCl2 ex. F2 ex. Zn + HCl AgCl ----> + NaCl ------> -----> NaF + + sodium fluoride Ag + Cl2 ZnCl2 + H2 Double Displacement Reactions A D.D reaction involves the exchange of __________ between two ionic compounds, usually in aqueous solution. They are double swap reactions, the two reactants trade places! There are three different forms of the D.D. reactions, we will talk about two: 1) Some ionic substances when mixed do not dissolve in water and a __________ is formed ( a solid that forms as a result of a chemical reaction). This reaction called a ____________ reaction Precipitate! ex. AgNO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) -----> ex. KI(aq) + AgCl (s) Pb(NO3)2(aq) ----> + NaNO3(aq) KNO3(aq) + PbI2(s) 2) Salt and water is formed. This is called a neutralization reaction. In this reaction an acid and a base react to form neutral water and a salt (ionic compound) ex. HCl(aq) + ex. H2SO4(aq) NaOH(aq) -----> H2O(l) + + KOH ----> K2SO4(aq) NaCl(aq) + H20(l) Combustion Reaction A Rapid reaction of a substance with __________. This releases energy in the form of heat and light. Mg + O2 ----> MgO + Energy (also synthesis) Substances with carbon and hydrogen form carbon dioxide and water as products. This results when oxygen is plentiful and is called complete combustion. (Blue Flame) For example: C3H8 (g) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) + H2O(g) Incomplete combustion results in production of carbon monoxide (poisonous gas) and/or soot (solid carbon), when oxygen is not plentiful. (Yellow Flame) For example: C4H10(g) + O2(g) -------> CO(g) + H2O(g) + energy