Contexts for Learning Key Stage 1
advertisement

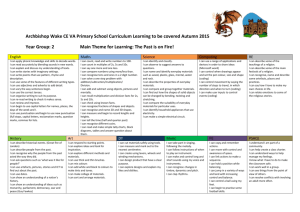
Lickey Hills Primary School Contexts for Learning Key Stage 1 Geography History Art & Design Breadth of study Breadth of study Breadth of study 6 2 localities: a The locality of the School b A locality with contrasting physical and/or human features either in the UK or Overseas 7a In the study of localities, pupils should: Study at a local scale b Carry out fieldwork investigations outside the classroom 6a Changes in pupils’ own lives and the way of life of their family or others around them b The way of life of people in the more distant past who lived in the local area or elsewhere in Britain c The lives of significant men, women and children drawn from the history of Britain and the wider world d Past events from the history of Britain and the wider world 5a Explore a range of starting points for practical work (Egg themselves, experiences, stories, natural and manmade objects and the environment) b Working independently and collaborating with others on projects in 2d and 3d and on different scales c Using a range of materials and processes (Egg painting, collage, print making, digital media, textiles, sculpture) d Investigating different kinds of art, craft and design (Egg in the locality, during visits, on the internet) Design Technology Breadth of study 5a Investigating and evaluating a range of familiar products (Egg talking about how they work, and whether they do what they are supposed to do) b Focused Practical Tasks that develop a range of techniques, skills, processes and knowledge c Designing and making assignments using a range of materials, including food, items that can be put together to make products, and textiles. - Music Breadth of study 5a A range of musical activities that integrate performing, composing and appraising b Responding to a range of musical and nonmusical starting points c Working independently and in groups of different sizes and as a class d A range of live and recorded music from different times and cultures NC programme of study PSHE & Citizenship Breadth of study 5a Opportunities to take and share responsibility b Feel positive about themselves c Take part in discussions d Make real choices e Meet and talk with people f Develop relationships through work and play g Consider social and moral dilemmas that they come across in everyday life h Ask for help Science RE ICT Breadth of study Breadth of study Breadth of study Learning should be related to pupil’s own thoughts, feelings and experience. Begin to understand Christianity and Judaism. Through a balance of the four strands: Beliefs Expression and celebration Living and belonging The search for meaning and purpose 5 Pupils will be taught the knowledge skills and understanding through: a Working with a range of information to investigate the different ways it can be presented; e.g. information about the sun being presented as a poem, picture or sound pattern. b Exploring a variety of ICT tools c Talking about the uses of ICT inside and outside school. 1 Use a range of domestic and environmental contexts, a range of sources and first hand and secondary data. 2 Use simple scientific language to communicate, name and describe. Recognise hazards, assess risks and take action to ensure health and safety. 1a Collect evidence by making observations and measurements when trying to answer a question. 2a Ask questions and decide how they might find the answer b Use first hand experience and information sources to answer questions c Think about what might happen before deciding what to do d Recognise when a test or comparison is unfair e Follow simple instructions to control risks f Explore using senses and record observations and measurements g Communicate what happens in a variety of ways h Make simple comparisons and identify patterns I Compare what happened, with expectations and explain J Review and explain work to others Knowledge & Understanding Knowledge & Understanding Knowledge and Understanding Knowledge & Understanding Knowledge & Understanding Knowledge and understanding Knowledge and understanding 1a Ask geographical questions b Observe and record c Express own views d Communicate in different ways 2a Use geographical language b Use fieldwork skills c Use globes maps and plans d Use secondary sources of information e make maps and plans 3a Identify and describe what places are like. b Identify and describe where places are 1a Place events and objects in chronological order b Use common words and phrases about the passing of time 1 Exploring and Developing Ideas a Record from firsthand evidence, experience and imagination b Ask and answer questions about starting points for work 1 a Generate ideas from experience b Develop ideas by shaping materials and putting together components c Talk about ideas d Plan by suggesting what to do next as ideas develop e Communicate ideas using a variety of methods, including drawing and models 1a Use voices to sing songs, chants and rhymes. b Play tuned and untuned instruments. c Rehearse and perform with others. 1 To develop confidence and responsibility and make the most of their abilities e.g. making class room rules, looking after pets. Recognising their achievements and being given positive feedback. 2.1 The differences between living and nonliving things. Life processes. Animals and plants in the local environment. 2.2 External parts of the body. Need for food and water. Exercise and keeping healthy. Drugs as medicine. Care of animals. Animal and human babies. Senses 2.3 Growth of plants. Parts of a plant. Seeds. 2.4 Group living things according to observable similarities and differences. 2.5 Plants and animals in the local environment. Similarities and differences between environments. Care of the environment. 3.1 Similarities and differences between materials. Sort by simple properties. Recognise and name common materials, their uses and why they are used for this. 3.2 Find out how the shape of some objects can be changed. Heating and cooling materials. 4.1 Appliances that use electricity. Simple circuits. The use of a switch to break a circuit. 4.2 Find out and describe movement. Pushes and pulls. Motion. 4.3 Light sources. Darkness. Sound and sound sources. Movement of sound and hearing. c Recognise how places have become the way they are and how they are changing d Recognise how places compare with other places e Recognise how places are linked to other places in the world. 4a Make observations about where things are located and about other features in the environment b Recognise changes in physical and human features 5a Recognise changes in the environment b Recognise how the environment may be improved and sustained 2a Recognise why people did things, why events happened and what happened as a result b Identify differences between ways of life at different times 3a Identify different ways in which the past is represented 4a Find out about the past from a range of sources b To ask and answer questions about the past 5a Select from their knowledge of history and communicate in a variety of ways. 2 Investigating and Making a Investigate the possibilities of a range of materials and processes b Try out tools and techniques, including drawing c Represent observations, ideas and feelings Design and make images and artefacts 3 Evaluating a Review what they and others have done and say what they think and feel about it b Say what they may change or improve in the future 4 Knowledge and understanding a Using visual and tactile elements, including colour, pattern, texture, line, tone, shape, form and space. b Materials and processes used in making art, craft and design c Differences and similarities in the work of artists, craftspeople and designers in different times and cultures. Paula Rudd - Lickey Hills Primary School 2006 2 a Select tools, techniques and materials from a range selected by the teacher b Explore the sensory qualities of materials c Measure, mark out, cut and shape d Assemble, join and combine materials e Use simple finishing techniques f Follow safe procedures for food safety and hygiene 3 a Talk about ideas, saying what they like and dislike b Identify what they could have done differently or how they could improve work in the future 4 a Learn about the working characteristics of materials (e.g. folding paper, plaiting yarn to make it stronger) b How mechanisms can be used in different ways (e.g. wheels and axels that allow movement) 2a Create musical patterns. b Explore, choose and organise sounds and musical ideas. 3a Explore ideas and feelings about music using movement, dance and musical language. b Make improvements to their own work 4a Internalise and recall sounds. b Know how the combined musical elements of pitch, duration, dynamics, tempo, timbre, texture and silence can be organised and used. c Know that sounds can be made in different ways and described using given and invented signs and symbols. d The purposes of music. 2 To prepare to play an active role as citizens E.g. Take part in discussions about issues. 3 To develop a healthy, safer lifestyle e.g. healthy meals 4 To develop good relationships and respecting the differences between people e.g. sharing, behaviour Knowledge and understanding Knowledge & Understanding Beliefs: Learn that Christians believe in God and they share this belief with other faiths. Key aspects of Christian belief relating to the life of Jesus and stories from the Old and New Testaments. Learn about the Jewish belief in God, about Tenakh, the Jewish scriptures, as a special book and key figures in Judaism. Expression and celebration: Worship and festivals in Christianity and Judaism. Visit to a local place of worship, buildings art, artefacts associated with worship. Living and Belonging: The ways in which religion affects lives, behaviour and relationships. Reflect upon feelings actions and codes of conduct at home and in school. Thinking of and respecting others. The search for meaning and purpose: Explore own identity, feelings and experiences and of others in the class and family. Reflect on questions about life and investigate some of the answers given by religious groups. Pupils should be taught how to: 1a Gather information from a variety of sources b Enter and store information in a variety of forms c Retrieve information that has been stored 2a To use text, tables images and sound to develop their ideas. b How to select from and add to information they have retrieved for particular purposes. c How to plan and give instructions to make things happen. d To try things out and explore what happens in real and imaginary situations. 3a How to share their ideas by presenting information in a variety of forms. b To present their completed work effectively. 4a Review what they have done b Describe the effects of their actions c Talk about what they might change in the future