Basic Chemistry Part 2 Handout
advertisement

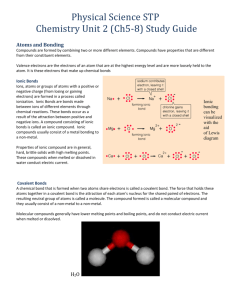
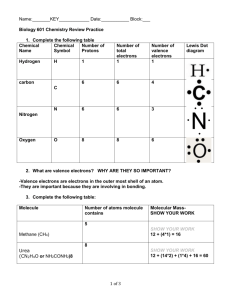
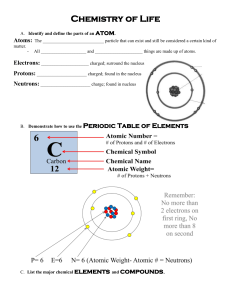
BASIC CHEMISTRY – Part 2 Name: Date: Pd: PART 1: MIXTURES: Fill in the blanks from the information provided on the presentation. A mixture is two or more substances blended together (not bonded). Each substance in a mixture keeps all of its chemical and physical properties. Mixtures, unlike compounds, can be separated into their individual substances by physical means. Example: salt and water can be separated by evaporation. A solution is a mixture of two or more substances, one dissolved in another. Two parts of a solution are the solute and the solvent. Solute – substance being dissolved Examples: sugar, salt Solvent – substance doing the dissolving Example: water A solution becomes saturated when the solvent holds all the solute that it can. It can no longer dissolve solute. Suspensions are a mixture of particles scattered throughout another. The particles do not dissolve. Examples: clouds, dust, fog, smoke, mud, blood Reflect: 1. Give another example of solutions including the solute and solvent. Vinegar and Calcium Carbonate, etc… 2. Can solutions be separated by chemical means? Perhaps, but will still involve physical separation as well PART 2: COMPOUNDS Compounds are two or more elements chemically joined by bonds. They are represented by chemical formulas. Properties of compounds are usually different than the atoms. Example: Hydrogen(gas) + Oxygen(gas) = Water (liquid) Example: Iron + Oxygen = Rust Compounds can be separated into their elements only if the chemical bonds are broken. This can be done by chemical means (chemical reaction) A molecule is the smallest part of a compound—like water—that has all the properties of the compound. PART 3: REVIEW COMPOUNDS AND ELEMENTS Write “E” for element or “C” for compound or B for BOTH for each description below: 1. __C__ Two or more elements combined 7. __C__ Water (H2O) 2. __E__ Made up of one type of atom 8. __B__ Smallest unit of a substance 3. __E__ Cannot be chemically broken down 9. __E__ Smallest unit of matter 4. __C__ Table Salt (NaCl) 10. __B__ Units of matter 5. __E__ Sodium (Na) 11. __E__ Hydrogen (H) 6. __C__ Glucose 12. __C__ Can be broken down chemically PART 4: FORMATION OF CHEMICAL BONDS A covalent bond is a bond formed when atoms share electrons to form a compound. Strong physical bond hydrogen oxygen 2 covalent bonds hydrogen H2O Molecule An ionic bond is formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. It is a weak electrical attraction, not a physical bond. Example: table salt (NaCl) Before 11 p+ 11 e0 After 11 p+ 10 e+1 Sodium (+) Chlorine (-) Before 17 p+ 17 e0 After 17 p+ 18 e-1 Instead of being neutral, atoms of sodium and chlorine making up salt become charged. Ions are charged atoms that have gained or lost one or more electrons. BASIC CHEMISTRY – Part 2 (page 2) Name: Answer Key Date: Pd: PART 5: CHEMICAL REACTIONS A chemical reaction is the process of breaking down existing chemical bonds of compound and forming new bonds. Elements combine in ways that cause their atoms to be stable. The energy required to start a chemical reaction is activation energy and the most common form of this energy is heat. A reaction that gives off more energy than it uses up is an exothermic reaction. A reaction that gives off less energy than it uses up is an endothermic reaction. Living things need a constant supply of energy from food because all cells use more energy than they produce. Example reactions: Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide Glucose (Sugar) + Oxygen. H2O + CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 Respiration (Breathing) Oxygen + food(glucose) water + carbon dioxide 6O2 + C6H12O6 H2O + CO2 Rusting, Burning, Digestion, etc… Reactants are on the left. Products are on the right. PART 6: QUESTIONS: 1. List and describe the major kinds of chemicals. Mixture – two or more blended substances Solution – A solute with a solvent dissolved in it Compound – two or more bonded substances 2. What is the difference between an ionic and covalent bond? Covalent bonds are strong physical bonds where atoms share electrons. Ionic bonds are weak electrical bonds where atoms transfer electrons. 3. Are mixtures formed during a chemical reaction? Why or why not? Mixtures are not formed during a chemical reaction because no bonds are being broken or formed. 4. How are mixtures, compounds, and chemical reactions important for living things? BASIC CHEMISTRY – Part 2 Name: Answer Key Date: Pd: PART 1: MIXTURES: Fill in the blanks from the information provided on the presentation. A mixture is two or more substances blended together (not bonded). Each substance in a mixture keeps all of its chemical and physical properties. Mixtures, unlike compounds, can be separated into their individual substances by physical means. Example: salt and water can be separated by evaporation. A solution is a mixture of two or more substances, one dissolved in another. Two parts of a solution are the solute and the solvent. Solute – substance being dissolved Examples: sugar, salt Solvent – substance doing the dissolving Example: water A solution becomes saturated when the solvent holds all the solute that it can. It can no longer dissolve solute. Suspensions are a mixture of particles scattered throughout another. The particles do not dissolve. Examples: clouds, dust, fog, smoke, mud, blood Reflect: 3. Give another example of solutions including the solute and solvent. Vinegar and Calcium Carbonate, etc… 4. Can solutions be separated by chemical means? Perhaps, but will still involve physical separation as well PART 2: COMPOUNDS Compounds are two or more elements chemically joined by bonds. They are represented by chemical formulas. Properties of compounds are usually different than the atoms. Example: Hydrogen(gas) + Oxygen(gas) = Water (liquid) Example: Iron + Oxygen = Rust Compounds can be separated into their elements only if the chemical bonds are broken. This can be done by chemical means (chemical reaction) A molecule is the smallest part of a compound—like water—that has all the properties of the compound. PART 3: REVIEW COMPOUNDS AND ELEMENTS Write “E” for element or “C” for compound or B for BOTH for each description below: 13. __C__ Two or more elements combined 19. __C__ Water (H2O) 14. __E__ Made up of one type of atom 20. __B__ Smallest unit of a substance 15. __E__ Cannot be chemically broken down 21. __E__ Smallest unit of matter 16. __C__ Table Salt (NaCl) 22. __B__ Units of matter 17. __E__ Sodium (Na) 23. __E__ Hydrogen (H) 18. __C__ Glucose 24. __C__ Can be broken down chemically PART 4: FORMATION OF CHEMICAL BONDS A covalent bond is a bond formed when atoms share electrons to form a compound. Strong physical bond hydrogen 8 8 oxygen 2 covalent bonds hydrogen H2O Molecule An ionic bond is formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. It is a weak electrical attraction, not a physical bond. Example: table salt (NaCl) Sodium Before 11 p+ 11 e0 After 11 p+ 10 e+1 Chlorine Before 17 p+ 17 e0 Transfer (+) (-) After 17 p+ 18 e-1 Instead of being neutral, atoms of sodium and chlorine making up salt become charged. Ions are charged atoms that have gained or lost one or more electrons. BASIC CHEMISTRY – Part 2 (page 2) Name: Answer Key Date: Pd: PART 5: CHEMICAL REACTIONS A chemical reaction is the process of breaking down existing chemical bonds of compound and forming new bonds. Elements combine in ways that cause their atoms to be stable. The energy required to start a chemical reaction is activation energy and the most common form of this energy is heat. A reaction that gives off more energy than it uses up is an exothermic reaction. A reaction that gives off less energy than it uses up is an endothermic reaction. Living things need a constant supply of energy from food because all cells use more energy than they produce. Example reactions: Photosynthesis Water + Carbon Dioxide Glucose (Sugar) + Oxygen. H2O + CO2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 Respiration (Breathing) Oxygen + food(glucose) water + carbon dioxide 6O2 + C6H12O6 H2O + CO2 Rusting, Burning, Digestion, etc… Reactants are on the left. Products are on the right. PART 6: QUESTIONS: 5. List and describe the major kinds of chemicals. Mixture – two or more blended substances Solution – A solute with a solvent dissolved in it Compound – two or more bonded substances 6. What is the difference between an ionic and covalent bond? Covalent bonds are strong physical bonds where atoms share electrons. Ionic bonds are weak electrical bonds where atoms transfer electrons. 7. Are mixtures formed during a chemical reaction? Why or why not? Mixtures are not formed during a chemical reaction because no bonds are being broken or formed. 8. How are mixtures, compounds, and chemical reactions important for living things?