8thgradeChemicalInteraction-StudyGuideANSWERSforUNITtest
advertisement

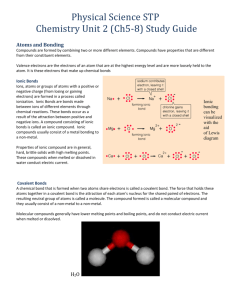
Name _____________________________________ Date __________ Chemical Interaction Unit Test - Study Guide 1. What are the parts of an atom? Nucleus which contains protons (+ charge) and neutrons (no charge) Surrounded by the electron cloud which contains the electrons (- charge) INCLUDE A DIAGRAM 2. How is the periodic table arranged? Past - by the atomic mass Present - by the atomic number (# of protons) and the properties of the element 3. What are the three main categories of elements on the periodic table? Metals - make up most of the elements located on the left, most are solid at room temp Non-metals - found on the right side of the table, most are gas at room temp Metalloids - zig zag separates metals and non-metals 4. What are the 3 types of bonds that hold compounds together?Describe each Ionic bonds - the transferring of ions Covalent bonds - the sharing of electrons Metallic bonds - freely sharing of electrons between metals INCLUDE DIAGRAMS OF EACH using the energy levels and the valence electrons 6. What determines the structure of a compound? The atoms and the type of bond holding the elements together 7. Describe in terms of energy what happens during all chemical reaction? During a chemical reaction energy can be released (exothermic reaction) or absorbed (endothermic reaction) as bonds are broken or new bonds or formed 8. Explain the Law of Conservation of Mass and the Law of Conservation of Matter Law of Conservation of Mass - The number of atoms present in the reactants is always equal to the number of atoms in the product Law of Conservation of Matter - The elements that are present in the reactants will be present in the product 9. Describe the 4 types of Reactions (Synthesis, Decomposition, Combustion and Replacement) Synthesis Reaction - Elements combine to form a chemical bond A + B → AB Decomposition Reaction - Compounds break down into simpler elements AB → A + B Combustion Reaction - one of the reactants will always be Oxygen (O2) and it will always produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) A + O2 → CO2 + H2O Replacement - Single Replacement - one element is replaced with another, single element reacting with a compound A + BC → B + AC Double Replacement - two elements switch, reactants contain compound reaction with compound AB + CD → AD + BD 10. Describe endothermic reaction and exothermic reaction Exothermic reaction - energy is release in a chemical reaction, the temperature will decrease Endothermic reaction - the energy is being absorbed, the temperature will increase 11. Balancing Chemical Equations - What are the parts of an equation? How do you read the arrow? reactants → products In a chemical equation you start with the reactants, through a chemical reaction they will create new substances or break apart. The arrow is read as “yields” Subscript will tell you how many atoms are present of that element, when balancing subscripts cannot be changed Coefficients are used to balance equations, they will also be used to tell the number of atoms present of each element 12. Balance the equation H2 + O2 → H2O 2H2 + O2 → 2H20 13. Define Solution A mixture that is the same throughout (homogeneous). It can be separated physically because it is not a chemical reaction 14. Describe the parts of a solution Solvent - the part of the solution that does the dissolving Solute - the part of the solution that gets dissolved Solvent dissolves the solute 15. What is the most common solvent? Water is known as the universal solvent 16. Why do some solutes dissolve in water but others solutes will not? Water is polar, so water will only dissolve other polar substances. If it is non-polar it will not dissolve. Substances need to have the same molecular structure. 17. Describe what happens if you change the CONCENTRATION of a solution. If the concentration of the solute is low the solution is said to be dilute. When the solution is holding the maximum amount of solute the solution is saturated, concentration of the solute is increased To increase the concentration more, you increase the temperature and slowly add more solute making the solution supersaturated. 18. What is an alloy? What is the process that makes these solutions alloys? What are some common alloys? An alloy is a mixture of metals. To mix them together they are melted into a liquid state, mixed, then slowly cooled. Common alloys: stainless steel, carbon steel, brass, nitinol, bronze, pewter 19. Describe how acids and bases can be neutralized If you combine an acid and a base they will neutralize, forming salt and water 20. Describe the characteristics of acids Acids are hydrogen donors litmus paper red low pH = High H+ sour, burn 21. Describe the characteristics of bases Bases are hydrogen ion acceptors litmus paper blue high pH = Low H+ bitter, slippery