Copy of Chem concept review practice (Key)
advertisement
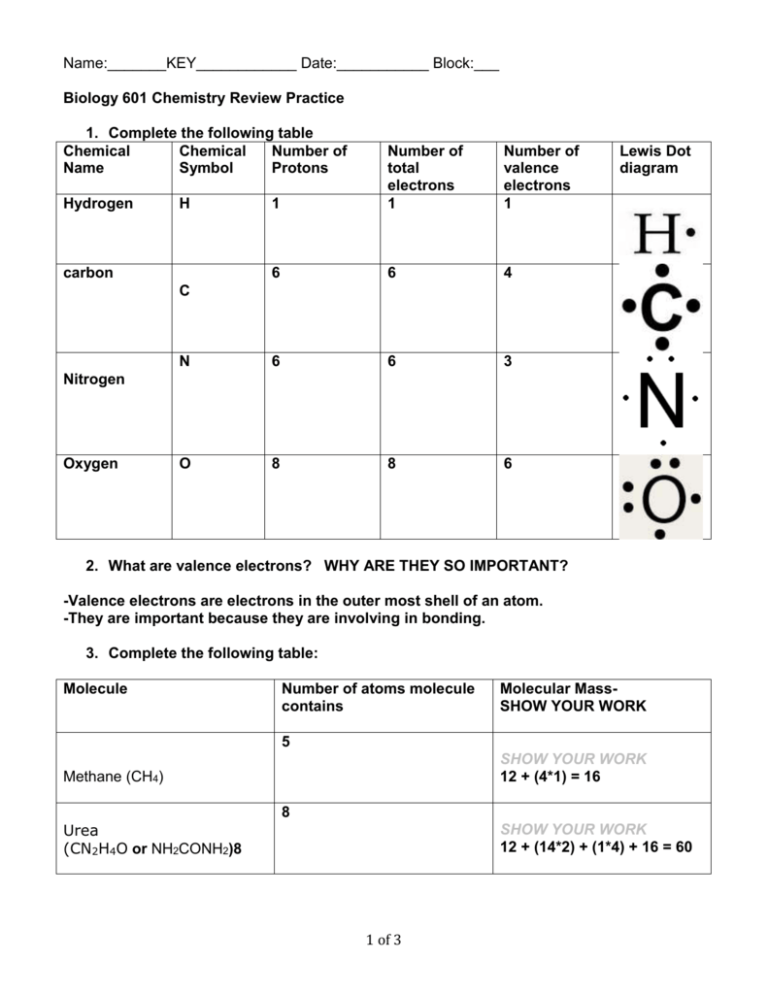
Name:_______KEY____________ Date:___________ Block:___ Biology 601 Chemistry Review Practice 1. Complete the following table Chemical Chemical Number of Name Symbol Protons Hydrogen 1 Number of total electrons 1 Number of valence electrons 1 6 6 4 N 6 6 3 O 8 8 6 H carbon Lewis Dot diagram C Nitrogen Oxygen 2. What are valence electrons? WHY ARE THEY SO IMPORTANT? -Valence electrons are electrons in the outer most shell of an atom. -They are important because they are involving in bonding. 3. Complete the following table: Molecule Number of atoms molecule contains Molecular MassSHOW YOUR WORK 5 SHOW YOUR WORK 12 + (4*1) = 16 Methane (CH4) 8 Urea (CN2H4O or NH2CONH2)8 SHOW YOUR WORK 12 + (14*2) + (1*4) + 16 = 60 1 of 3 4. Compare and contrast the following intramolecular forces: ionic bonds, polar covalent and nonpolar covalent bonds. -Ionic Bond: Attraction between oppositely charged ions. Occurs between metals and non-metals. -Polar covalent bond: The electrons are shared between the two atoms. Polarity exist because the two atoms has high electronegativity difference between them. -Nonpolar covalent bond: The electrons are shared between the two atoms. Electrons are equally shared between two atoms. 5. Define electronegativity. -Electronegativity shows how much an atom “grabs” onto it’s electrons. 6. Using the periodic table, complete the following chart. Bonded Electronegativity Bond type (ionic, polar or nonpolar) elements difference O-N 0.5 covalent Show the polarity of the bond by drawing an arrow from the positive to negative side on the bond between the 2 elements (i.e. ) Towards O K-Cl 2.8 ionic bond Towards Cl C- H 0.4 non-polar covalent bond N/A 9. Label the picture of the water molecule below: a. To show which elements have a slight + charge and which elements have a slight charge. b. Draw more water molecules and use dashed lines to show the maximum number of hydrogen bonds one water molecule can make. a. Hydrogens has slightly positive and oxygen has slight negative charge 2 of 3 b. 7. Circle or highlight where the following molecule, Serine, is capable of making hydrogen bonds. Places capable for hydrogen Bonds: NH2, COOH, OH 8. What are the parts of a solution? -The Solute: substance that is dissolved -The Solvent: substance that solute can dissolve in. 9. What is solubility? -a property that tells us how a substance can dissolve in a solvent. 10. Which salt solution is more concentrated, solution A, which contains 18g of salt in 6L of water, or solution B, which contains 24g of salt in 12L of water? -Solution A is more concentrated because there is more percentage of solute dissolved in the solvent. 11. Define pH. Describe an acid and a base. Draw the pH scale, labeling neutral, acidic, and basic regions. -pH measures the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution -Acid examples: lemon juice, vinegar Base example: blood, baking soda 3 of 3


![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-300x300.png)