GEOG 1112: Weather and Climate
advertisement

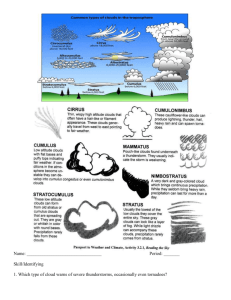
GEOG 1112: Weather and Climate Summer 2008 I. Identify the following terms: A. air pressure B. cyclone C. anticyclone D. isobars E. pressure gradient force F. coriolis force G. friction force H. geostrophic wind I. rossby waves J. polar jet stream K. subtropical jet stream L. ITCZ M. Monsoon N. Gyre O. Thermohaline circulation P. Gulf Stream Q. Bermuda-Azores High R. ENSO S. Western intensification T. Surface tension U. Capillary action V. Maximum humidity W. Specific humidity X. Relative humidity Y. Saturation Z. Evapotranspiration AA. Adiabatic processes BB. Lifting condensation level CC. Environmental lapse rate DD. Condensation nuclei EE. Hygroscopic aerosol FF. Heterogeneous nucleation GG. Freezing rain HH. Hail II. Snow JJ. Clouds KK. Fog LL. Advection fog MM. Radiation fog NN. Sea fog OO. Evaporation fog PP. Culumonibus cloud Exam 2 Study Guide QQ. Nimbostratus cloud RR. Cirrocumulus cloud SS. Altocirrus cloud TT. Air mass or air parcel UU. mP air mass VV. cP air mass WW. cT air mass XX. mT air mass YY. rainshadow ZZ. winward AAA. leeward BBB. midlatitude cyclone CCC. occluded front DDD. stationary front EEE. warm front FFF. cold front GGG. squall line HHH. cloud to cloud lightning III. cloud to ground lightning JJJ. Thunder KKK. Tornado LLL. Suction vortex MMM. Tropical wave NNN. Storm surge OOO. Eye wall PPP. eye II. Short Answer: A. Explain the movement of wind during the day and at night in the mountain-valley breeze. B. Explain how the Gulf Stream transports heat from the Caribbean to northern Europe. C. Explain why relative humidity gives no indication as to whether or not it will rain. D. Explain why condensation forms on the outside of a glass of ice water. E. Explain what happens to the internal temperature, size, internal pressure, and density of an air parcel as it rises and falls in the atmosphere. F. Explain the relationship between air temperature, water vapor content of the air, and altitude of an area. G. Remembering that the DAR is 10°C/1000m, would an unsaturated air parcel at the surface having an internal temperature of 10°C rise in an atmosphere if the outside temperature was 8°C (ELR: 3°C/1000m). Explain your answer. H. Explain the differences between cirrus, altus, stratus, and cumulus clouds. I. List and describe the 4 lifting mechanisms. J. Name and describe the 4 stages of midlatitude cyclone development. K. Explain the difference between an air mass thunderstorm and a supercell (severe) thunderstorm. L. Why are there more tornadoes in the US than any other country? M. What are the 3 conditions necessary for hurricane formation? III. Illustrations A. Illustrate a high-pressure cell and a low-pressure cell under the influence of a) the pressure gradient force, b) the pressure gradient force and coriolis force, and c) the pressure gradient force, coriolis force, and friction force for the Northern Hemisphere. B. Attach the three cell model of global circulation to your study guide. C. Illustrate the land-sea breeze. D. Illustrate the oceanic-atmospheric circulation of the tropical Pacific during a normal year and during an ENSO year. Include the following in your illustration: names and direction of winds, upwelling, downwelling, pressure cells, western intensification. E. Illustrate the Hydrologic Cycle. Include the following in your diagram: evaporation, clouds, advection, transpiration, evapotranspiration, infiltration, percolation, run-off. F. Be able to illustrate the source regions of the major air masses affecting US weather. G. Illustrate a warm front and a cold front. Include air masses involved, clouds formed, and arrows indicating movement of air masses.