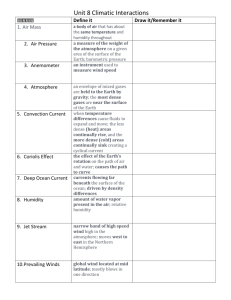
study me!!!!!
advertisement
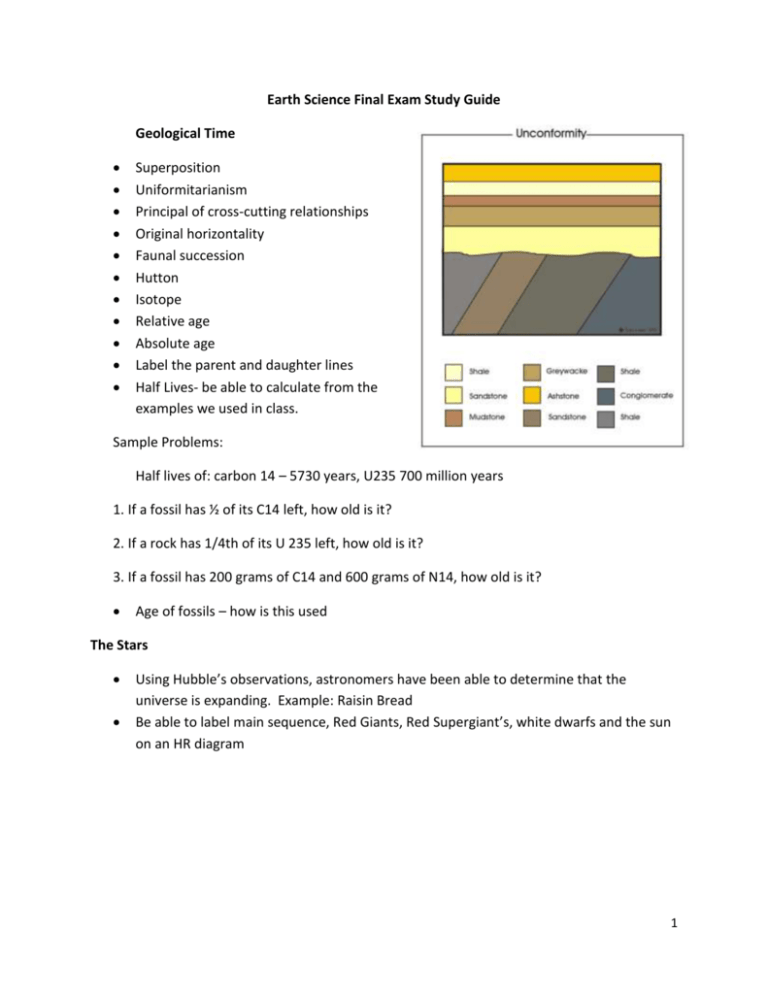
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide Geological Time Superposition Uniformitarianism Principal of cross-cutting relationships Original horizontality Faunal succession Hutton Isotope Relative age Absolute age Label the parent and daughter lines Half Lives- be able to calculate from the examples we used in class. Sample Problems: Half lives of: carbon 14 – 5730 years, U235 700 million years 1. If a fossil has ½ of its C14 left, how old is it? 2. If a rock has 1/4th of its U 235 left, how old is it? 3. If a fossil has 200 grams of C14 and 600 grams of N14, how old is it? Age of fossils – how is this used The Stars Using Hubble’s observations, astronomers have been able to determine that the universe is expanding. Example: Raisin Bread Be able to label main sequence, Red Giants, Red Supergiant’s, white dwarfs and the sun on an HR diagram 1 Nebula Giant Supergiant’s Planetary Nebula White Dwarfs Nova Supernova Neutron star Pulsar Black Hole Astronomy Asteroid Belt Asteroids Meteoroids Meteorites Comets 75% of sun’s mass is hydrogen 25% of sun’s mass is helium 1% other Nuclear Fusion The energy released in the three steps of nuclear fusion causes the sun to shine and gives the sun its high temperature 2 Layers of the Sun: o The Center of the Sun is the Core o Radiative Zone o The Convective Zone o Convection o Photosphere o Chromosphere o Corona Sunspot Prominences Solar Flares Coronal Mass Ejection Auroras Atmosphere Atmosphere Elements in the air and their percentages o Nitrogen o Oxygen o Argon Photosynthesis Ozone Ozone Layer Particulates Atmosphere pressure decreases as altitude increases As temperature increases, atmospheric pressure at sea level decreases Layers of the Atmosphere o Troposphere o Tropopause o Stratosphere o Mesosphere o Mesopause o Ionosphere o Thermosphere Temperature Invasion Scattering Albedo 3 Greenhouse Effect The absorption of thermal energy from the ground heats the lower atmosphere and keeps Earth’s surface much warmer than it would be if there were no atmosphere Continuous cycle Prevailing Winds Coriolis Effect Trade Winds Westerlies Polar Easterlies Front Jet Streams Doldrums Breeze Sea Breeze Land Breeze Valley Breeze Mountain Breeze 4 Atmospheric Pressure Latent Heat When liquid evaporates, the water…. Evaporation Sublimation Humidity Dew point Absolute humidity Mixing ratio Equation used to measure absolute humidity Why do meteorologists prefer to describe humidity using mixing ratio of air Relative Humidity Psychrometer What is the difference between the two thermometers of a psychrometer What happens to the wet bulb thermometer when the psychrometer is whirled around Clouds and Fog Cloud Evaporation Fog What must be available for water vapor to condense and form a cloud What is present in troposphere that is essential for cloud formation What condition must the air be for a cloud to form Adiabatic cooling Adiabatic Lapse Rate Condensation level Results of air being forced upwards How do large clouds associated with storm systems form What two features classify clouds Three basic forms of clouds Stratus clouds Nimbus mean? Cumulus Cirrus and cirro Compare and contrast fog and clouds 5 Precipitation Rain Drizzle Snow Sleet Glaze Ice Ice Storm Hail What two processes cause cloud droplets to fall to Earth Coalescence What happens during supercooling What creates supercooling Rain Gauge Measuring stick Doppler Radar Three things meteorologists can determine with a Doppler Radar 6