Solubility Rules
advertisement

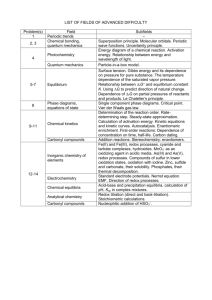
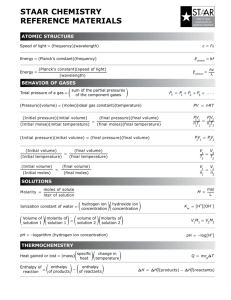
Solubility Rules The following compounds are soluble: 1) 2) 3) 4) All common group 1A and NH4+ compounds. All common NO3- (nitrate), CH3COO- (acetate), ClO4- (perchlorate) compounds. All common Cl-, Br-, I- compounds, except those of Ag+, Pb2+, Cu+, and Hg22+ (mercurous). All common SO42- (sulfate) compounds, except those of Ca2+, Sr2+, Ba2+, and Pb2+. The following compounds are insoluble: 1) All common metal hydroxides, except those of group 1A and the larger members of group 2A (starting with Ca2+). 2) All common carbonates (CO32-) and phosphates (PO43-), except those of group 1A and NH4+. 3) All common sulfides (S2-), except those of group 1A, group 2A, and NH4+. ______________________________________________________________________ Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers General rules: 1) 2) 3) 4) All atoms in their elemental form have an O.N. of zero (i.e. Na, Cl2, and O2). All monatomic ions have an O.N. equal to the ion charge (Na+ [O.N.=+1], O2[O.N.=-2]). The sum of the oxidation numbers for atoms in a compound equals zero. The sum of the oxidation numbers for atoms in a polyatomic ion equals the charge on the polyatomic ion. Specific rules: 1) 2) 3) Group 1A: Group 2A: Hydrogen: 4) 5) Fluorine: Oxygen: 6) Group 7A: O.N. = +1 in all compounds. O.N. = +2 in all compounds. O.N. = +1 when combined with any nonmetal. O.N. = -1 when combined with any metal and boron. O.N. = -1 in all compounds. O.N. = -1 in peroxides (i.e. H2O2, Na2O2). O.N. = -2 in all other compounds. O.N. = -1 when combined with any atom, except oxygen and a halogen higher in the group.