File
advertisement
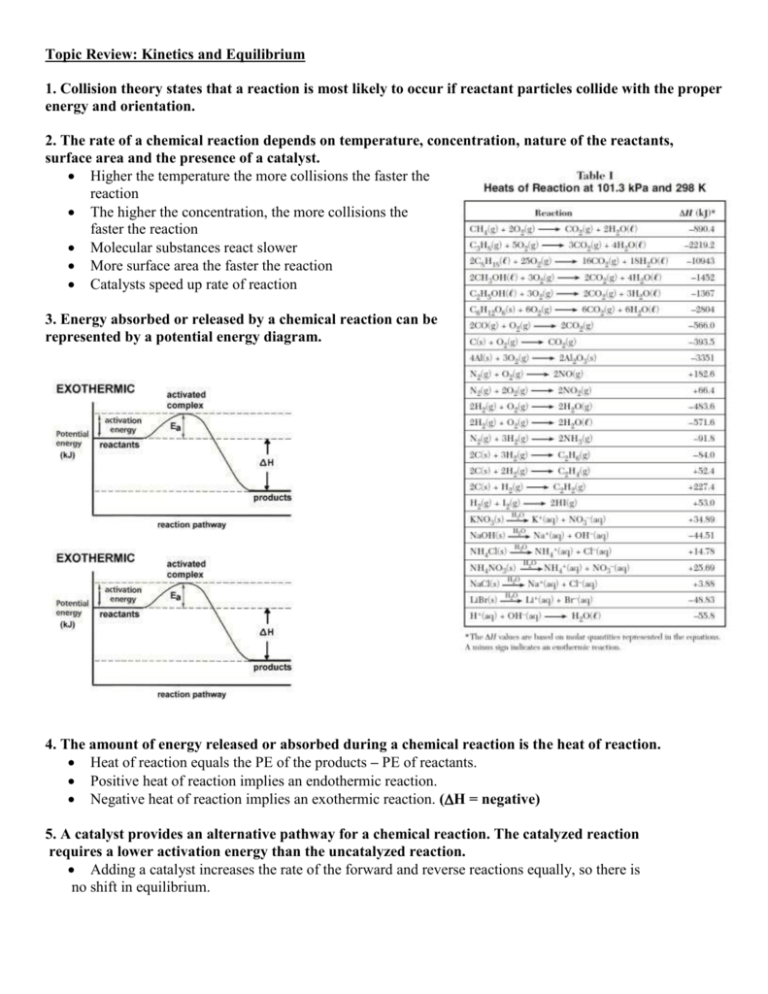
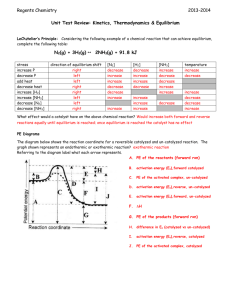
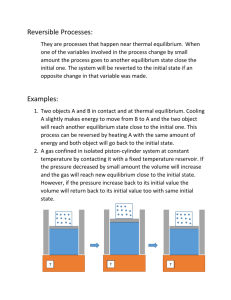
Topic Review: Kinetics and Equilibrium 1. Collision theory states that a reaction is most likely to occur if reactant particles collide with the proper energy and orientation. 2. The rate of a chemical reaction depends on temperature, concentration, nature of the reactants, surface area and the presence of a catalyst. Higher the temperature the more collisions the faster the reaction The higher the concentration, the more collisions the faster the reaction Molecular substances react slower More surface area the faster the reaction Catalysts speed up rate of reaction 3. Energy absorbed or released by a chemical reaction can be represented by a potential energy diagram. 4. The amount of energy released or absorbed during a chemical reaction is the heat of reaction. Heat of reaction equals the PE of the products – PE of reactants. Positive heat of reaction implies an endothermic reaction. Negative heat of reaction implies an exothermic reaction. (H = negative) 5. A catalyst provides an alternative pathway for a chemical reaction. The catalyzed reaction requires a lower activation energy than the uncatalyzed reaction. Adding a catalyst increases the rate of the forward and reverse reactions equally, so there is no shift in equilibrium. 6. Entropy is a measure of the randomness or disorder in a system. A system with greater disorder has greater entropy. More mess, higher entropy, not related to temperature There is an increase in entropy from slg There is an increase in entropy from saq There is a increase in entropy going from less parts to more parts 7. Systems in nature tend to undergo changes towards lower energy (H) and higher entropy (S). Exothermic and more mess 8. Exothermic reactions that result in increased entropy are spontaneous. 9. At equilibrium the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction for both physical and chemical changes. Phase Equilibrium – equilibrium between phase changes (sl and lg) Solution Equilibrium – must be a saturated solution (saq) These reactions must be stoppered, a closed system 10. The measurable quantities of reactants and products remain constant at equilibrium. Concentrations or quantities constant, rates equal 11. LeChatelier’s principle can be used to predict the effect of stress on a system in equilibrium. Stresses include a change in pressure, volume, concentration, and temperature. Add away, remove towards Increase pressure favors the side with the least number of moles Increase temperature favors the endothermic Increase concentration equilibrium shifts away from the increase Removal – equilibrium shifts towards the side that was reduced Increase volume causes decrease in pressure favors most moles. Practice: Use the graph to answer the following questions 1. What is the heat of reactants? a) 30 kJ b) 40 kJ c) 100 KJ d) 60 kJ c) 20 KJ d) 60 kJ 2. What is the heat of the products? a) 30 kJ b) 100 kJ 3. What is the heat of the activated complex for the reaction? a) 30 kJ b) 100 kJ c) 20 KJ d) 60 kJ 4. What is the ∆H of this reaction? a) + 20 kJ b) -100 kJ c) -20 KJ d) +60 kJ c) both d) neither 5. What type of reaction is this? a) exothermic b) endothermic 6. Draw a dashed curved line on the above diagram to indicate what the PE curve would look like if a catalyst was added to this reaction, using the catalyzed reaction line as your guide. 7. When a system becomes less random the entropy a. Increases b. decreases 8. Which shows an increase in entropy? b. H2O(s) H2O(l) b. H2O(g) H2O(l) c. remains the same c. H2O(l) H2O(s) 9. The following reactions shows the entropy CaCO3(s) CaO(s) and CO2(g) c. Increases b. decreases c. remains the same 10. The following reactions shows the entropy 2AB 2A+B2 d. Increases b. decreases c. remains the same 11. A chemical reaction is spontaneous if e. There is a gain of energy and entropy increases f. There is a gain of energy and entropy decreases g. There is a loss of energy and entropy increases h. There is a loss of energy and entropy decreases Use the graph to answer the following questions: 12. Label where equilibrium is achieved in the system. 13. Write an equation for the system at equilibrium. 14. In the equation: PCl5(g) + 100kJ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) Describe what happens to the chlorine when the following stressors are added to the system at equilibrium: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. PCl5 is added PCl3 is added PCl5 is removed PCl3 is removed Heat is added Heat is removed Pressure is added Pressure is relieved The volume of the chamber is decreased The volume of the chamber is increased k. A catalyst is added ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________