Kinetics, Thermodynamics & Equilibrium
advertisement

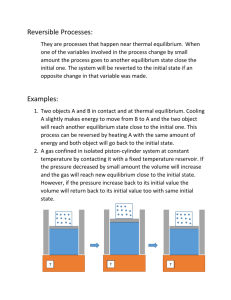
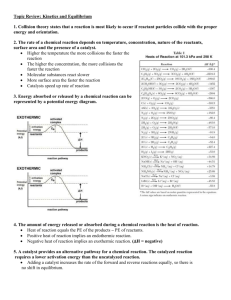
Regents Chemistry 2013-2014 Unit Test Review: Kinetics, Thermodynamics & Equilibrium LeChâtelier’s Principle: Considering the following example of a chemical reaction that can achieve equilibrium, complete the following table: N2(g) + 3H2(g) stress increase P decrease P add heat decrease heat increase [H2] increase [NH3] decrease [N2] decrease [NH3] 2NH3(g) + 91.8 kJ direction of equilibrium shift right left left right right left left right [N2] decrease increase increase decrease decrease increase [H2] decrease increase increase decrease increase increase increase increase [NH3] increase decrease decrease increase increase decrease temperature increase decrease increase decrease decrease increase What effect would a catalyst have on the above chemical reaction? Would increase both forward and reverse reactions equally until equilibrium is reached; once equilibrium is reached the catalyst has no effect PE Diagrams The diagram below shows the reaction coordinate for a reversible catalyzed and un-catalyzed reaction. The graph shown represents an endothermic or exothermic reaction? exothermic reaction Referring to the diagram label what each arrow represents. A. PE of the reactants (forward rxn) B. activation energy (Ea),forward catalyzed C. PE of the activated complex, un-catalyzed D. activation energy (Ea),reverse, un-catalyzed E. activation energy (Ea),forward, un-catalyzed F. ΔH G. PE of the products (forward rxn) H. difference in Ea (catalyzed vs un-catalyzed) I. activation energy (Ea),reverse, catalyzed J. PE of the activated complex, catalyzed What are the two driving forces in nature? enthalpy and entropy Enthalpy: Heat energy H - nature prefers low energy (least amount of energy – think couch potato) Entropy: randomness, disorder, chaos - S nature prefers high entropy Nature will favor reactions that: 1. go from high E to low E (exothermic reaction) 2. go from low entropy to high entropy } will be spontaneous chemical reactions are always spontaneous when energy ↓ and chaos ↑ ΔH is - and ΔS is + chemical reactions are never spontaneous when energy ↑ and chaos ↓ ΔH is + and ΔS is - chemical reactions are sometimes spontaneous when temperature is high and ΔH is - and ΔS is - energy ↓ and chaos ↓ ΔH is + and ΔS is + energy ↑ and chaos ↑ Do the following changes involve an increase or a decrease in entropy? 1. evaporating water : H2O(l) ↔ H2O(g) 2. freezing water: H2O(l) ↔ H2O(s) increase in entropy decrease in entropy 3. dissolving salt in water: NaCl(s) ↔ H2O(aq) increase in entropy answer key for multiple choice Q: Q# answer Q# answer Q# answer Q# answer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 B D C C C A D C C B B B C B D 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 D D B B B A A B B C C B B B D 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 D A D B A A B C B C C D B C B 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 B D C B C C A B A A B A B