Thermo, Kinetics, Equilibrium
advertisement

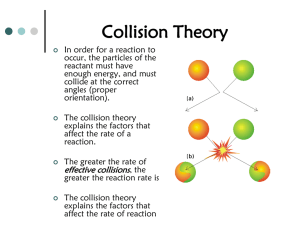
Test Objectives: Thermodynamics, Kinetics & Equilibrium Use Collision Theory to describe how chemical reactions occur Describe the difference between effective & ineffective collisions Know the 6 factors that influence reaction rate Describe how changes in temp, pressure, concentration & surface area affect reaction rate Describe how the nature of the reactants influences reaction rate Describe how the presence of a catalyst affects reaction rate Be able to write thermochemical equations for endothermic and exothermic reactions Draw, label & interpret potential energy diagrams for both endothermic & exothermic reactions o Be able to Label: PE of reactants, products & activated complex Activation energy of forward & reverse reactions Heat of reaction Be able to indicate the effect of a catalyst on a PE diagram Be able to calculate the heat of reaction (∆H) given the heat of the products & the heat of the reactants Be able to tell from the ∆H if a reaction is endothermic or exothermic Use table I to determine the stability of the compounds listed Define enthalpy, entropy, & spontaneity Know under what conditions a change will always be spontaneous or never be spontaneous Understand what factors increase or decrease entropy Given a thermochemical equation for a chemical or physical change be able to predict the spontaneity by assessing the signs of ∆H & ∆S Define equilibrium & describe in terms of the forward & reverse reaction rates Describe what happens to the concentrations of reactants & products in a chemical system at equilibrium Understand that equilibrium occurs in a closed system Be able to list the 3 types of equilibrium & give examples of each State Le Chatelier’s Principle & apply it to equilibrium systems Know what a stressor is & how it will affect a chemical system Be able to explain these terms with respect to a chemical equation : Shift to the Right , Shift to the Left Be able to explain how pressure changes affect gas-phase chemical systems at equilibrium Be able to explain how temperature changes affect both endothermic & exothermic chemical systems at equilibrium Be able to predict how changes in the concentration of a reactant or product will affect the equilibrium concentrations of a system