molecular
advertisement
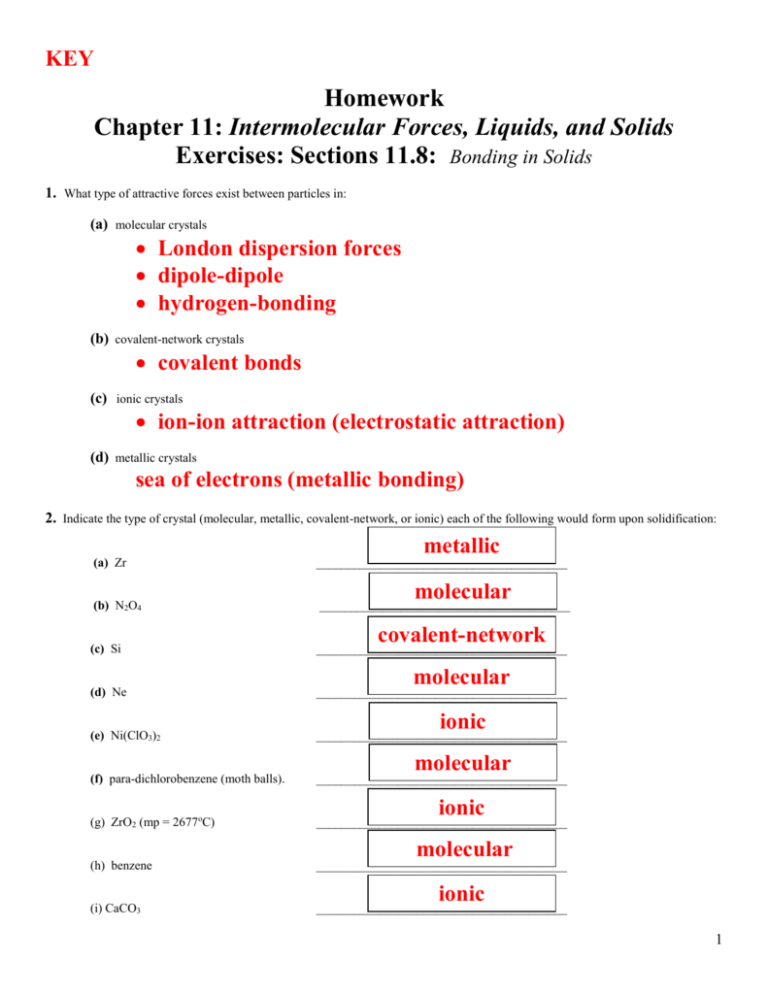
KEY Homework Chapter 11: Intermolecular Forces, Liquids, and Solids Exercises: Sections 11.8: Bonding in Solids 1. What type of attractive forces exist between particles in: (a) molecular crystals London dispersion forces dipole-dipole hydrogen-bonding (b) covalent-network crystals covalent bonds (c) ionic crystals ion-ion attraction (electrostatic attraction) (d) metallic crystals sea of electrons (metallic bonding) 2. Indicate the type of crystal (molecular, metallic, covalent-network, or ionic) each of the following would form upon solidification: metallic (a) Zr ________________________________________ (b) N2O4 ________________________________________ (c) Si ________________________________________ (d) Ne ________________________________________ (e) Ni(ClO3)2 ________________________________________ (f) para-dichlorobenzene (moth balls). ________________________________________ (g) ZrO2 (mp = 2677oC) ________________________________________ (h) benzene ________________________________________ (i) CaCO3 ________________________________________ molecular covalent-network molecular ionic molecular ionic molecular ionic 1 3. Covalent bonding occurs in both molecular and covalent-network solids. Why do these two kinds of solids differ so greatly in their hardness and melting points? Molecular Solids Covalent Network Crystal = individual molecules held together by relatively weak IMF = no individual molecules, all atoms are covalently bonded to one another to make a large network crystal 4. Which type (or types) of crystalline solid is characterized by each of the following: (a) high mobility of electrons throughout the solid; metallic (b) softness, relatively low melting point; molecular (c) high melting point and poor electrical conductivity; (d) charged particles throughout the solid; covalent-network or ionic ionic 5. You are given a white substance that sublimes at 3000oC; the solid is a nonconductor of electricity and is insoluble in water. Which type of solid (Table 11.7 on page 464 of the textbook) might this substance be? NOT metallic b/c not a conductor NOT molecular b/c very high melting point probably NOT ionic b/c it's not soluble MOST LIKELY covalent-network 8. For each of the following compounds, predict which will have the higher melting point and indicate why? (a) NaF, MgF2; 2+ b/c Mg vs Na+ ; stronger attraction between ions (b) HF, HCl; HF = has H-bonding as additional IMF to overcome b/c HCll = does NOT have H-bonding (c) C (graphite), CO; b/c C is a covalent-network crystal w/ covalent bonds; CO = only weak IMFs (d) Kr, Ar. b/c its larger molar mass means stronger London dispersion forces 2