Ionic & Molecular Solids Lab: Properties & Bonding
advertisement

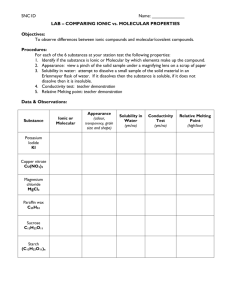
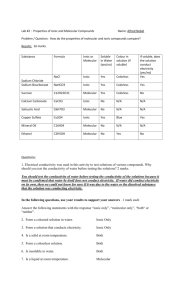
SNC2D Name: PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF IONIC AND MOLECULAR SOLIDS Certain compounds are made of molecules in which their atoms are held together by covalent bonds. These compounds are called molecular solids because they are made of molecules as opposed to ions. Other compounds are made up of a network of negative anions and positive cations, arranged in such a way that each positive ion is surrounded exclusively by negative ions and vice-versa. The solid is held together due to the attraction between the positive and negative charges, thus forming a crystal lattice. These solids are called ionic compounds. Purpose To examine the physical properties molecular and ionic solids. Questions How does the type of chemical bonding (ionic / molecular) affect: 1. melting point? 2. solubility in water? 3. electrical conductivity as a solid? 4. electrical conductivity in aqueous solution? Hypothesis Create an “If… then …” statement to predict one of the above questions. Each pod of 4 students will answer all of the questions; you will be responsible for one. If the solid is ionic, then its _______________ will be (higher than / lower than / the same as) a molecular solid. The rationale for this hypothesis is __________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Materials safety goggles 2 small beakers glass stirring rod scoopula beaker tongs tea light conductivity tester distilled water Epsom Salts (MgSO4) rock salt, NaCl(s) flour, C6H10O5(s) sucrose, C12H22O11(s) Apparatus Draw a proper scientific diagram of the equipment and materials used in your investigation. SNC2D Name: Procedure Design your own procedure to test your variable and get it approved by the teacher before commencing your investigation. Be clear and specific. Consider safety and waste disposal/clean up. Observations Epsom Salt (MgSO4) Rock Salt (NaCl(s)) Flour (C6H10O5(s)) Sucrose (C12H22O11(s)) Type of solid (ionic / molecular) Physical properties (appearance/ colour / texture / hardness) Odour (strong / weak / none) Melting point (high / low) Solubility in water (very soluble / slightly soluble / insoluble) Conductivity of solid (good / poor) Conductivity of solution (good / poor) Analysis Questions 1. Which solid had the strongest odour? What does this tell you about the forces holding the particles of the solid together? (Hint: What is odour? How does odour reach our noses?) 2. According to your observations regarding melting points, in which solid are the molecules held more tightly together? Explain with reference to the particle theory of matter. 3. Which compound was a better conductor as a solid? Using your knowledge of chemical bonds and/or additional research, support your answer. 4. Which compound was a better conductor as a solution? Using your knowledge of chemical bonds and/or additional research, support your answer. 5. Predict the results of the tests your group performed for iron (III) sulphate, Fe2(SO4)3(s). Justify your predictions. Discussion Discuss the sources of error in your experiment. What could you have changed to make your investigation work better?