Geography LN.2 – INTERIOR OF THE EARTH
advertisement

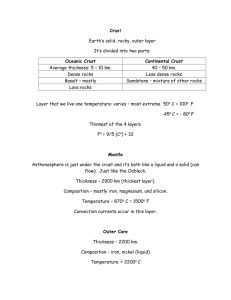
GEOGRAPHY LN.2 – INTERIOR OF THE EARTH OUTCOMES OF FOCUSED LEARNING: The Structure of the earth Crust: Sial & Sima – Mantle – Core Rocks and Minerals Igneous Rocks – Sedimentary Rocks – Metamorphic Rocks Rock Cycle KEY TERMS: 1. Fossils: The dead remains of plants and animals trapped within layers of rocks 2. Lava: Magma which has come onto the earth’s surface 3. Magma: Molten rock found below the crust 4. Minerals: Natural inorganic compounds found in the earth’s crust 5. Ores: Rocks containing metals in large quantities, which can be extracted economically 6. Rock Cycle: The cycle of transformation which rocks undergo 7. Rocks: Rocks formed by the cooling of lava 8. Sediment: Fine particles that come from the disintegration of rocks and are carried and deposited by wind, water, ice, etc. 9. Crevices: Narrow opening 10. Igneous rocks: Rocks formed by the cooling of lava 11. Sedimentary rocks: Rocks formed by the accumulation of sediment 12. Metamorphic rocks: Rocks that have changed from their original form under extreme temperature and pressure 4. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN ONE OR TWO SENTENCES: a. Name the three layers of the earth. The three layers of the earth are crust, mantle and core. b. What is magma? Magma is the molten rock found below the crust. c. What is lava? The rocks that are formed when magma breaks through the crust and reaches the surface of the earth (where it is called lava). d. What is a mineral? Minerals are natural inorganic substances which contain one or more elements and which have definite physical and chemical properties. e. Mention any three uses of rocks. Rocks are useful in many ways – (i) as building materials, (ii) sources of metals like iron, copper etc. (iii) yield valuable gems such as diamonds, jade (emerald), etc. 5. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN FOUR OR FIVE SENTENCES: a. Explain the difference between sial and sima. SIAL SIMA I.Upper part of the crust. I.Lower part of the crust. II.Composed of minerals like II.Minerals that make it are silica and aluminium. silica and magnesium. III.Average density – 2.7 III.Average density – 3.0 b. Describe the core of the earth. CORE: I.Centre part of the earth (also known as the barysphere). II.Average density – 10 to 12. III.Made up of nickel(Ni) and iron (Fe) and is therefore referred to as ‘nife’. IV.The pressure on the core is extremely high and the temperature is estimated to be 3,0000C to 60000C. V.Inner core – solid; Outer core – liquid. c. What do you know about igneous rocks? I.Igneous rocks are also called primary rocks, as they are formed first because of the cooling of magma. They are of two types: II.1. Extrusive or volcanic rocks are formed when magma breaks through the crust and reaches the surface of the earth (lava). Ex: Basalt and obsidian. III.2. Intrusive or plutonic rocks are formed when magma fails to break through the crust and cools slowly close under the crust forming rocks. Ex.: Granite and dolerite. d. What is the rock cycle? I.The rock cycle is a continuous process in which rocks change from one kind into another. II.Igneous rocks are also called primary rocks, as they are formed first because of the cooling of magma. III.Due to weathering broken material gets deposited on the floor of the oceans, seas, rivers and lakes to form sedimentary rocks. IV.Sedimentary rocks under extreme heat and pressure change into metamorphic rocks. V.Again, under extreme heat and pressure, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks melt to form magma, from which igneous rocks are formed. Thus the rock cycle continues. e. Explain the formation of metamorphic rocks with examples. FORMATION OF METAMORPHIC ROCKS: I.When igneous and sedimentary rocks are subjected to great heat and pressure, their original character and appearance completely change, giving them a new form. II.Examples: Marble, Quartzite, etc. III.Limestone changes to form marble, sandstone changes to form quartzite etc. LN.3 – EARTH MOVEMENTS & MAJOR LANDFORMS OUTCOMES OF FOCUSED LEARNING: Folding Faulting Volcanoes Earthquakes KEY TERMS: 1. Plates: division of crust into several large slabs of rocks 2. Magma: molten material inside the earth 3. Fissure: crack or gap through which magma oozes out 4. Richter Scale: the scale used for measuring the earthquake 5. Seismograph: Instrument used for the measurement of the quakes 6. Seismologists: People who study earthquakes 7. Seismology: Study of earthquakes 4. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN ONE OR TWO SENTENCES: a. What do you understand by plate tectonics? The study of the movements of the earth’s plates and the associated phenomena is plate tectonics. b. What is folding? Folding is the wave-like upliftment of sedimentary rocks due to horizontal forces from two opposite sides. c. What is a rift valley? A rift valley is a sunken portion of land between two block mountains. Examples: Deccan plateau d. What causes the formation of block mountain? Block mountains are formed when the land between the two faults or cracks is uplifted by internal forces. Examples: The Vindhya, The Satpura e. What do you understand by the focus of an earthquake? The point where the earthquake waves originate inside the earth is called the focus of the earthquake. 5. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS IN FOUR OR FIVE SENTENCES: a. What is a fold mountain? FOLD MOUNTAIN: A fold mountain is formed due to folding or wave-like upliftment of sedimentary rocks due to horizontal forces from two opposite sides. This happen when a part of the crust is pushed against another. Examples: The Himalayas, The Aravallis. b. Explain the formation of a block mountain. FORMATION OF A BLOCK MOUNTAIN: Due to tension vertical faults or cracks are created along the lines of weakness in the crust. Sometimes the land between the cracks is uplifted by internal forces, forming a block mountain or horst. Examples: The Vindhya, The Satpura c. How is a rift valley formed? FORMATION OF A RIFT VALLEY: A rift valley is created when a part of the crust between two faults sings down. The land on either side of the valley remains standing as block mountains. Examples: The Himalayas, The Aravallis. d. Describe a volcano with a suitable diagram? VOLCANO: Volcanoes are openings in the earth’s crust through which molten minerals, ash and hot gases are thrown out. a. Magma Chamber: A large underground pool of molten rock below the crust b. Vent: The opening through which the magma comes onto the surface c. Crater: A bowl-shaped depression at the mouth of the volcano d. Lava flow: A mass of flowing or molten lava e. What is an earthquake? What causes it? EARTHQUAKE: Earthquakes are vibrations or tremors felt on the surface of the earth. The tremors are caused due to disturbances beneath the crust. These disturbances could either be due to plates colliding or rubbing against each other or due to volcanic eruptions. The point where the earthquake waves originate inside the earth is called the focus of the earthquake. The tremors or vibrations produced during an earthquake are also called seismic waves.