Earth`s Structure
advertisement

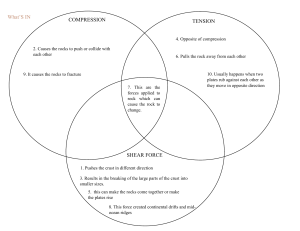
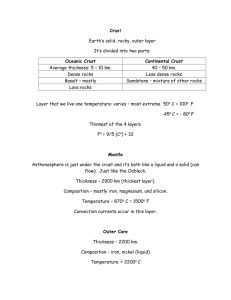
Earth’s Structure - formed 4.6 billion years ago - James Hutton (1700’s) , believed that the earth was much older than thought to be, and that the earth’s surface had changed over time -Uniformitarianism – geologic processes occurring today are that same as in the past The Science of Geology - Study of the planet earth including its composition and structure - 2 types of forces: 1. Constructive (shape earth by mountain building and other land areas like islands) 2. Destructive ( slowly wear away land features) A Cross Section of Earth - Layers are divided based upon composition of materials - Temperature and pressure increase with depth - The Crust - rocky outer layer of crust Majority of rocks are made of silicon and oxygen ( silicates ) Often contain metals of Al, Fe, Ca Continental Crust – less dense rocks such as granite ( 8 – 75 Km thick ) Oceanic Crust – dense rocks like basalt ( @ 7 Km thick ) - The Mantle Hot but solid rock, 2,850 Km to the core, composed of silicates rich in magnesium 3 layers: Lithosphere – cool, rigid rock, 100 Km, Asthenosphere soft weak rock, flows, mesosphere strong rock - The Core Large sphere of metals ( mostly iron and nickel ) Outer core – 2,260 Km, liquid, creates earths’ magnetic field Inner core – 1,220 Km, solid due to extreme pressure (3.6 million times the pressure at earth surface ), 5,500 0C ( almost surface of sun temperature)