Notes 3.5 Active Transport
advertisement

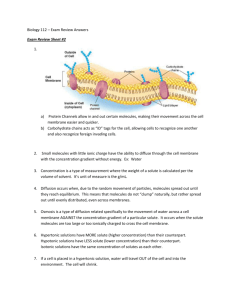
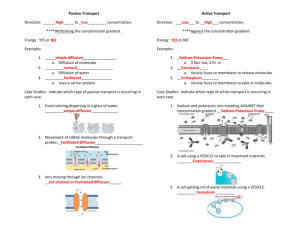
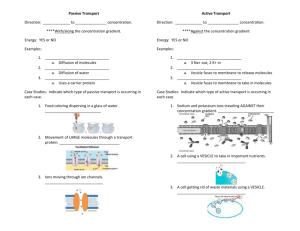
Notes # ______ Date _________ How Molecules Naturally Move 1. Molecules are constantly in Motion – Kinetic energy. Molecules in solids - vibrate in place. Molecules in liquids and gases - move freely. 2. Molecules move randomly colliding as they move. 3. Molecules move from areas of high concentration to where they are less concentrated along their concentration gradient. Concentration Gradient –the difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another. Concentration Gradient of Color Concentration – the number of molecules of a substance in a given volume. The amount of solute / amount of solvent. Random movements of molecules along their concentration gradient eventually cause them to spread out evenly. This is called dynamic equilibrium which means that the concentration is the same throughout(equilibrium) but that the molecules continue to move (it’s dynamic!). What example did we see? ___________________________________ Wait! If the molecules of perfume continued to spread out evenly, why can’t they smell the perfume downstairs??? ______________________________________________ Two variables that affect the rate of molecular movement are: 1. ________________________ 2.________________________ Notes # ______ Date _________ METHODS OF TRANSPORT: HOW MATERIALS CROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE CELL Section 3.4 Passive Transport: Diffusion, Facilitated Diffusion and Osmosis Key Concept: Some molecules move on their own into or out of cells because of concentration differences on opposite sides of the membrane without the cell using energy. This is called Passive Transport. Methods of Passive Transport - Do Not Require Cell to Use Energy 1. Diffusion – Net (overall) movement of molecules from area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 2. Facilitated “Helper” Diffusion – Movement of material through the cell membrane by a “helper” transport protein (channel or carrier) that binds specifically to the molecule 3. Osmosis – Diffusion of water molecules through a membrane from an area of higher water concentration to one of lower water concentration. Super Important Factoid: Higher water concentration in solution means lower solute concentration Lower water concentration in solution means higher solute concentration Comparing Solutions: Isotonic – solutions have the same solute and water concentrations Hypertonic – Solution has a Higher solute concentration (less water concentration) Hypotonic – Solution has a Lower solute concentration (more water concentration) Notes # ______ Date _________ Section 3.5: Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis Key Concept: Cells use energy to transport materials across the cell membrane Methods of Active Transport - Require Cell Energy: 1. Transport Protein / Membrane pumps *Moves molecules across membrane from low to high concentration areas *Involves a transport molecule that spans the cell membrane *Transport molecule binds to 1 or 2 specific target molecules *Binding causes the transport molecule to change shape and move the molecules *The ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule transfers E to the transport protein molecule giving it the E it needs to do to move molecules through the cell membrane. 2. Endocytosis - Taking in of materials by engulfing them in a vesicle Phagocytosis – Cell membrane engulfs large particles or whole organisms ex. White blood cell engulf a bacteria, Amoeba engulfs paramecium Pinocytosis – Cell membrane engulfs liquid droplets 3. Exocytosis – Release of substances from by fusing vesicle with membrane ex. Secretory vesicles. Unicellular organism excreting waste.