Plasma Membrane: Structure & Transport Guided Notes
advertisement

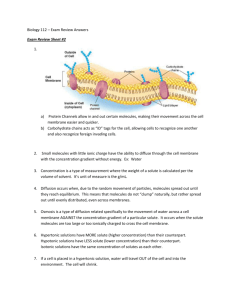
PLASMA MEMBRANE GUIDED NOTES Name: ________________________________ PLASMA MEMBRANE Selectively permeable barrier between the cell and the environment. What does ‘selectively permeable’ mean? _________________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Selective permeability is necessary for the cell to maintain the correct internal environment for physiological functions. PLASMA MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Phospholipids ◦ Make up the majority of the membrane ◦ Arranged in a bilayer, with hydrophilic heads outside, and hydrophobic tails inside Hydrophilic = ______________________ Hydrophilic molecules are __________________ like water. Hydrophobic = _____________________ Hydrophobic molecules are _________________ like oil. ____________________________ can interact with watery external environment and watery cytoplasm. ____________________________ reduce the diffusion of water and other charged or polar substances across the membrane. 1 Cholesterol ◦ Makes the cell membrane more ______________ and less _________________________________________________ Proteins ◦ Act as _________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Glycoproteins and Glycolipids ◦ Glyco = ___________________________ ◦ Influence cell interactions (e.g. identifying cell as ‘self’) and molecule transport CELL MEMBRANE TRANSPORT VOCABULARY __________________ a dissolving agent (water, usually) __________________ substances dissolved in a solution __________________ watery environment outside cells __________________ lower solute concentration ________________ higher solute concentration ________________ equal solute concentration TRANSPORT MECHANISMS Transport of materials across the cell membrane can be characterized as passive or active. Passive mechanisms require __________________________ from the cell. ALL passive mechanisms transport molecules ____________________________________________. Active mechanisms require _________________ from the cell. 2 PASSIVE TRANSPORT Diffusion is the _________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________. Results from the random movement of molecules. Simple Diffusion ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________. Only works for tiny OR non-polar molecules. Examples: fats, fat-soluble vitamins, O2, CO2, Cl Osmosis is ________________________________________________________. Facilitated diffusion - __________________________________________________; used for large polar molecules ◦ Example: glucose Filtration occurs when water and solutes are pushed __________________________ _____________________________________________________________________. 3 Water and solutes move down pressure gradient. Process by which blood is filtered in the kidney. ACTIVE TRANSPORT Active transport requires _________________________________to transport material across the cell. Active transport is used for ◦ Solutes moving ________________________the concentration gradient - or ◦ Very_______________ substances Solute Pumping (aka active transport) Membrane proteins (called solute pumps) ______________________to carry solutes _______________________their concentration gradient. Examples: amino acids and most ions Exocytosis - movement of materials _________________________ by vesicle Examples: hormones, neurotransmitters, mucus, some wastes Endocytosis – movement of materials ______________________ by vesicle o Phagocytosis (cell eating) – white blood cells engulf bacteria, dead cells, and foreign debris o Pinocytosis (cell drinking) - used to take up droplets of fats and dissolved proteins 4