Chapter 4 Chemistry of Life Section 4 Homeostasis and transport
advertisement

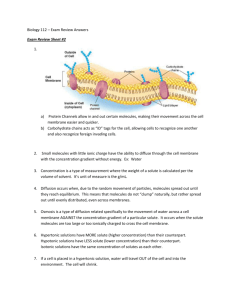
Chapter 4 Chemistry of Life Section 4 Homeostasis and transport: Passive transport the movement of substances across a membrane without energy Diffusion: The simplest form of active transport Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration The difference of concentration is called the concentration gradient Example: a sugar cube is drop in water and goes to the bottom, as it dissolves it spreads out from the bottom to the top Diffusion is driven by kinetic energy Molecules are in constant motion Molecules tend to move down a concentration gradient Equilibrium concentration of molecules of a substance is the same throughout even at equilibrium molecules are in constant motion Diffusion across a membrane: cell membrane allows certain materials to pass in and out of the cell ability of a molecule to move depends on size and shape molecules that dissolve in lipids can pass freely ( carbon dioxide and oxygen) Osmosis: Solution is a solute dissolved in a solvent The solute is the material being dissolved, solvent is material doing the dissolving Example: sugar water, sugar is solute water is solvent together they are a solution In the case of cells solutes are organic and the solvent is water Water diffuses across the membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration Because water moves down the concentration gradient a cell does not need to expend energy Direction of osmosisnet direction depends on the amount of solutes on the two sides of the membrane 1. Hypotonic solution Concentration of solute in the cell is higher than concentration outside the cell 2. Hypertonic solution concentration of solute outside the cell is higher in than the concentration in the cell 3. isotonic concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside of the cell Facilitated Diffusion: Some molecules are so large they can not pass easily through a membrane Transport proteins are imbedded in the membrane and act like a fast food window letting large molecules into the cell and out of the cell without using energy Active transport The movement of molecules across a membrane with energy used 1. Endocytosis- the movement of large molecules into the cell by surrounding the material with part of the cell membrane 2. Exocytosis- the movement of large molecules out of the cell by surrounding the material with part of the cell membrane Section Review: 1. Explain how cell membranes are selectively permeable? 2. Compare and contrast the processes of osmosis and diffusion. 3. Why are endocytosis and exocytosis important processes in cells? Critical thinking: Why are fresh fruits and vegetables sprinkled with water at produce markets?