Cell Transport Test Review--KEY - Level
advertisement
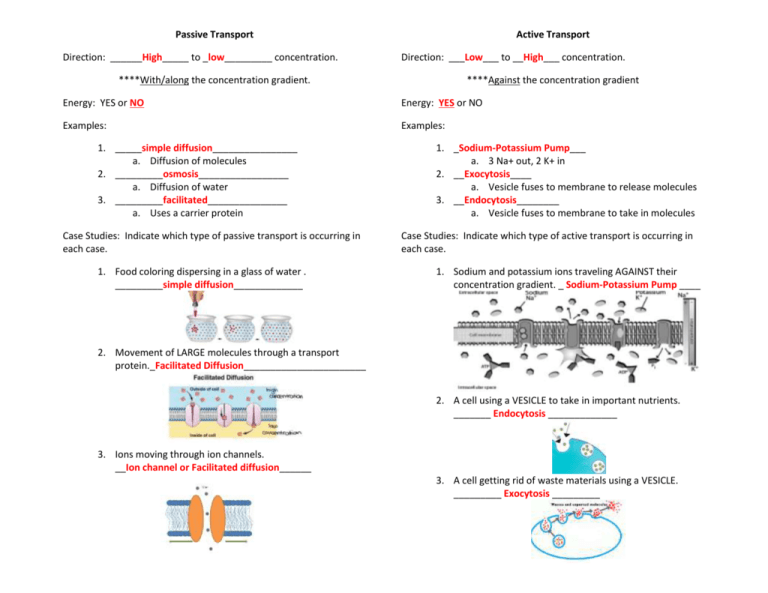
Passive Transport Direction: ______High_____ to _low_________ concentration. Active Transport Direction: ___Low___ to __High___ concentration. ****With/along the concentration gradient. ****Against the concentration gradient Energy: YES or NO Energy: YES or NO Examples: Examples: 1. _____simple diffusion________________ a. Diffusion of molecules 2. _________osmosis_________________ a. Diffusion of water 3. _________facilitated_______________ a. Uses a carrier protein Case Studies: Indicate which type of passive transport is occurring in each case. 1. Food coloring dispersing in a glass of water . _________simple diffusion_____________ 1. _Sodium-Potassium Pump___ a. 3 Na+ out, 2 K+ in 2. __Exocytosis____ a. Vesicle fuses to membrane to release molecules 3. __Endocytosis________ a. Vesicle fuses to membrane to take in molecules Case Studies: Indicate which type of active transport is occurring in each case. 1. Sodium and potassium ions traveling AGAINST their concentration gradient. _ Sodium-Potassium Pump ____ 2. Movement of LARGE molecules through a transport protein._Facilitated Diffusion_______________________ 2. A cell using a VESICLE to take in important nutrients. _______ Endocytosis _____________ 3. Ions moving through ion channels. __Ion channel or Facilitated diffusion______ 3. A cell getting rid of waste materials using a VESICLE. _________ Exocytosis _________ Solutions Homeostasis and the Membrane 1. The type of molecules that makes up the lipid bilayer is a _ phospholipid __ molecule. 2. The outside of the lipid bilayer is _hydrophilic_ (loves water) and the inside is _hydrophobic__ (hates water). 1. The solute is _ Sugar __________ ( the substance being dissolved) 2. The solvent is __ Water_________________ ( the substance that does the dissolving) 3. A _ Solution _____ is the mixture of the solute and the solvent. 3. The cell membrane also contains _proteins_ and __ carbohydrates__. Types of solutions: Cell A B C 4. Solution A is __ Isotonic Solution _____ A. A cell in this solution will __ be at steady state __ 5. Solution B is __ Hypertonic Solution ____ A. A cell in this solution will __ Shrivel/Shrink ____ 6. Solution C is ___ Hypotonic Solution ___ A. A cell in this solution will __ Swell and Burst __ 4. The cell membrane is _selectively__ _permeable__ which allows the cell to control what enters and leaves. This maintains the HEALTH of the cell. 5. Membranes help to maintain _homeostasis or equilibrium_ (steady state) by regulating the movement of molecules. 6. Molecules will eventually become BALANCED / UNBALANCED on both sides of the membrane. Practice Questions 1. Explain the process illustrated in the diagram. High Concentration Fluid OUTSIDE the cell has: Lower water molecule concentration (high solute) Then the fluid is: Water will diffuse: ??? Out of the cell How the cell is affected: Shrink ____ 13. 3. The term missing from the chart above is A. hypertonic. C. isotonic. B. hypotonic. D. equilibrium. Low Concentration 4. Which of the following is not part of the cell membrane? A. Passage of water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane to equalize concentration. B. Movement of molecules against a concentration gradient expanding energy. C. Separation of suspended particles from fluid environment through a porous membrane. D. Transport of molecules across a membrane from a high to low concentration gradient by means of a carrier molecule. 2. How does the cell membrane in the drawing below help to maintain the health of this cell? A. B. C. D. By providing support and structure for the cell. By manufacturing protein to provide energy for the cell. By regulating the transport of materials in and out of the cell. By storing food as future energy for the cell. A. B. C. D. carbohydrates phospholipids Nucleic acids cholesterol 5. The interior of the plasma membrane is A. hydrophobic B. hydrophilic C. polar D. concentrated