Cell
advertisement

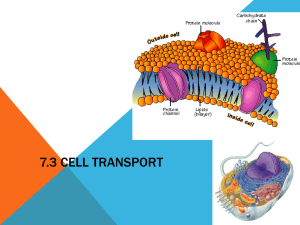
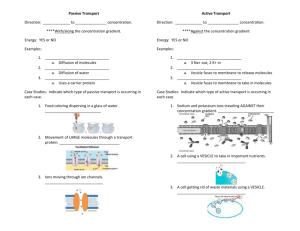
Notes # ______ Date _________ METHODS OF TRANSPORT: HOW MATERIALS CROSS THE CELL MEMBRANE How Molecules Naturally Move 1. Molecules are constantly in Motion – Kinetic energy. 2. Molecules move randomly colliding as they move. 3. Molecules move from areas of high concentration to where they are less concentrated along their concentration gradient. Concentration Gradient – Diffenrence in concentration of a substance across space. Section 3.4 Diffusion and Osmosis Key Concept: Some materials can move in and out of cells through their membranes without the cell using energy. This is called Passive Transport. Methods of Passive Transport - Do Not Require Cell to Use Energy 1. Diffusion – Net (overall) movement of molecules from area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 2. Facilitated “Helper” Diffusion – Movement of material through the cell membrane by a “helper” transport protein (channel or carrier) that binds specifically to the molecule 3. Osmosis – Diffusion of water molecules through a membrane from an area of higher water concentration to one of lower water concentration. Notes # ______ Date _________ Section 3.5: Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis Key Concept: Cells use energy to transport materials that cannot diffuse across the cell membrane on their own. Methods of Transport Requiring Cell Energy: 1. Active Transport (Membrane pumps)*Moves molecules across membrane from low to high concentration areas *Involves a transport molecule that spans the cell membrane *Transport molecule binds to 1 or 2 specific target molecules *Binding causes the transport molecule to change shape and move the molecules *The ATP (adenosine triphosphate) molecule transfers E to the transport protein molecule giving it the E it needs to do to move molecules through the cell membrane. 2. Endocytosis - Taking in of materials by engulfing them in a vesicle Phagocytosis – Cell membrane engulfs large particles or whole organisms ex. White blood cell engulf a bacteria, Amoeba engulfs paramecium Pinocytosis – Cell membrane engulfs liquid droplets 3. Exocytosis – Release of substances from by fusing vesicle with membrane ex. Secretory vesicles. Unicellular organism excreting waste. Notes # ______ Date _________