Cornell Notes pgs. 61-65 Rocks What is a rock? A rock is a naturally
advertisement
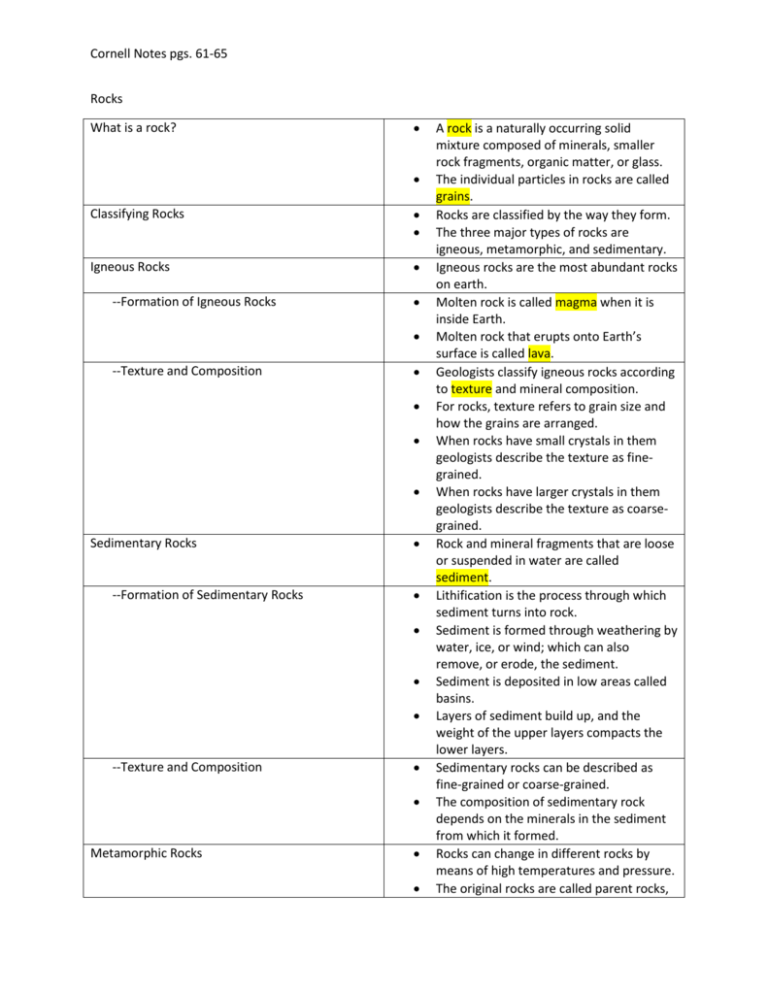
Cornell Notes pgs. 61-65 Rocks What is a rock? Classifying Rocks Igneous Rocks --Formation of Igneous Rocks --Texture and Composition Sedimentary Rocks --Formation of Sedimentary Rocks --Texture and Composition Metamorphic Rocks A rock is a naturally occurring solid mixture composed of minerals, smaller rock fragments, organic matter, or glass. The individual particles in rocks are called grains. Rocks are classified by the way they form. The three major types of rocks are igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary. Igneous rocks are the most abundant rocks on earth. Molten rock is called magma when it is inside Earth. Molten rock that erupts onto Earth’s surface is called lava. Geologists classify igneous rocks according to texture and mineral composition. For rocks, texture refers to grain size and how the grains are arranged. When rocks have small crystals in them geologists describe the texture as finegrained. When rocks have larger crystals in them geologists describe the texture as coarsegrained. Rock and mineral fragments that are loose or suspended in water are called sediment. Lithification is the process through which sediment turns into rock. Sediment is formed through weathering by water, ice, or wind; which can also remove, or erode, the sediment. Sediment is deposited in low areas called basins. Layers of sediment build up, and the weight of the upper layers compacts the lower layers. Sedimentary rocks can be described as fine-grained or coarse-grained. The composition of sedimentary rock depends on the minerals in the sediment from which it formed. Rocks can change in different rocks by means of high temperatures and pressure. The original rocks are called parent rocks, Cornell Notes pgs. 61-65 --Formation of Metamorphic Rocks --Texture and Composition --Foliated Metamorphic Rocks --Nonfoliated Metamorphic Rocks Rocks in Everyday Life and the new rocks are called metamorphic rocks. Metamorphic rocks form when parent rocks are squeezed, heated, or exposed to hot fluids. They remain solid, but the texture, and sometimes the mineral, composition of the parent rock change and this process is called metamorphism. The textures of most metamorphic rocks result from increases in temperature and pressure. The mineral composition of metamorphic rocks might be the result of minerals that are present in the parent rock, or they might grow in the new metamorphic rock. Foliation results when uneven pressures cause flat minerals to line up, giving the rock a layered appearance. These types of rocks do not exhibit foliation. Rocks are abundant natural resources that are used in many ways based on their physical characteristics.







