5.5 Atoms and Ions.fill
advertisement

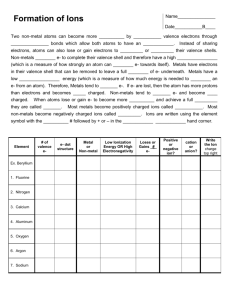
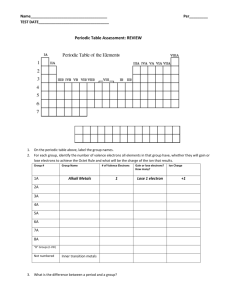
Atoms and Ions If we look at the number of valence electrons of any given atom and see that it is full, then the atom is stable. If not then it needs to react with some other element to achieve stability. Atoms are neutral, ______________________________________________. Many times when scientists refer to substances found in our body, like sodium found in our blood, they are not referring to the shiny metal sodium, they are referring to the _____________________________. Ions are charged atoms. Atoms become charged ___________________________________ (metals) or _______________________________ (non-metals). Why are ions formed? So elements can obtain a full valence shell, stability! (the ultimate goal in chemistry!) A Positive Ion is called a ______________, a negative ion is called an ____________________. Why do metals lose valence electrons to become positive ions? Metals have a low number of valence electrons (1,2 or 3). It is easier for them to ___________________ rather than for them to gain, 7,6 or 5 to have a full valence shell of 8. Why do non-metals gain valence electrons to become negative ions? Non-Metals have a high number of valence electrons (4,5,6 or 7). It is easier for them to ______________________ rather than lose. *Elements like the easy route when deciding to lose or gain their valence electrons, check and see what is easiest for them to do. How do we know that metals lose and non-metals gain? lets look at some examples: Na O Hint: When drawing the Bohr-Rutherford diagram of an ion, draw the atom first and then the ion. Charges of ions on the periodic table: Group 1 +1 Valence e- Group 2 +2 Group 13 +3 Group 14 +/- 4 Group 15 -3 Group 16 -2 Group 17 -1 Group 18 0