acid
advertisement

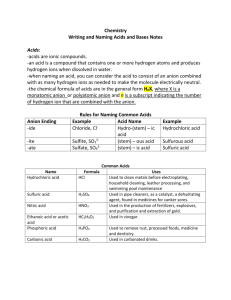
KEY Sample Questions for Chapter 14: Acids and Bases 14.1 Acids and Bases 1. (Read pgs. 442-446 in the chemistry textbook) (a) What does it mean to say a solid substance has dissolved in water? the individual particles of the solid have been completely surrounded by water molecules (b) What does it mean for a chemical to dissociate (ionize) in aqueous solution? some of the solid that dissolves produces ions 2. (a) What is an electrolyte? substances which will produce ions when they dissolve - the resulting solution will conduct an electric current b) What are strong electrolytes? substances for which 100% of the particles ionize in aqueous solution - the resulting solution is a strong conductor of electricity (c) What are weak electrolytes? substances for which less than 100 % of the particles will ionize in aqueous solution - the resulting solution is a weak conductor of electricity (d) what is a nonelectrolyte? a substance which dissolves in water but produces no ions the resulting solution is a nonconductor of elctricity 1 3. (a) Fill in the following table of electrolytes: Summary of Electrolytic Behavior of Common Soluble Ionic and Molecular Compounds Compound Strong Electrolyte Weak Electrolyte Nonelectrolyte Ionic All None None Molecular Strong Acids Weak Acids Weak Bases All other compounds (b) What happens if an ionic substance is insoluble in water? it is considered a weak electrolyte, b/c some miniscule amount WILL dissolve and ionize 100% .....but, b/c such a small amount dissolves there there will not be many ions in the solution 4. Identify each of the following as a strong, weak, or nonelectrolyte based on their chemical formulas. i. CO2 non vi. NH4CH3COOH strong ii. KNO3 strong vii. LiBr strong iii. C2H6 non viii. XeF2 non iv. Mg(OH)2 weak ix. PbSO4 weak v. NaCl strong x. Ca3(PO4)2 weak 5. Identify the non-, strong, and weak electrolytic solutions below. Explain your choices. strong electrolyte 100% ionized weak electrolyte < 100% ionized nonelectrolyte no ions 2 6. (a) What is the hydronium ion? it is a water molecule which has an extra hydrogen atom (b) What is the symbol for the hydronium ion? H3O+ 7. usually shortened to just H+ (a) What is the hydroxide ion? it is a water molecule which has lost one of its electrons (b) What is the symbol for the hydroxide ion? OH − 8. What is an acid? a substance that dissociates in water and causes an increase in the concentration of hydronium ion, [H+]*, of the aqueous solution *NOTE: brackets indicate concentration in molarity, thus [H+] means the concentration of H+ ion in moles per liter 9. What is a base? a substance that dissociates in water and causes an increase in the concentration of hydroxide ion, [OH−] 10. The table of electrolytes from Question 3(a) identifies strong acids as strong electrolytes. What are the strong acids? 1. HCl hydrochloric acid 5. HClO3 chloric acid 2. HBr hydrobromic acid 6. HClO4 perchloric acid 3. HI hydroiodic acid 7. H2SO4 sulfuric acid 4. HNO3 nitric acid ALL other acids are weak acids - meaning they are weak electrolytes 3 11. Write a dissociation equation for the following strong and weak acids. STRONG ACIDS: HCl(aq) → H+(aq) + Cl−(aq) (a) HCl(aq) (b) HNO3(aq) HNO3(aq) → H+(aq) + NO3− (aq) (c) H2SO4(aq) H2SO4(aq) → 2H+(aq) + SO42− (aq) WEAK ACIDS: HF(aq) (a) HF(aq) H+(aq) + F−(aq) (b) HNO2(aq) HNO2(aq) H+(aq) + NO2− (aq) (c) H2SO3(aq) H2SO3(aq) 2H+(aq) + SO32− (aq) a double arrow is used because weak electrolytes do not stay dissolved......the undissolved part is always in equilibrium with the dissolved part 12. All the strong bases are ionic compounds and, therefore, strong electrolytes. What are the strong bases? 1. LiOH lithium hydroxide 2. NaOH sodium hydroxide 3. KOH potassium hydroxide 4. RbOH rubidium hydroxide 5. CsOH cesium hydroxide 6. Ca(OH)2 calcium hydroxide 7. Sr(OH)2 strontium hydroxide 8. Ba(OH)2 barium hydroxide 4 13. Write a dissociation equation for the following strong and weak Bases. STRONG BASES: LiOH(s) → Li+(aq) + OH−(aq) (a) LiOH(s) Ca(OH)2(s) → Ca2+(aq) + 2 OH− (aq) (b) Ca(OH)2(s) WEAK BASES: (a) Mg(OH)2(s) (b) Sr(OH)3(s) Mg(OH)2(s) Mg2+(aq) + 2 OH−(aq) Sr(OH)3(s) Sr3+(aq) + 3 OH−(aq) 14. The ammonium polyatomic ion, NH4+(aq), dissociates weakly to increase the [H+] in aqueous solution. Write an equation to show the dissociation of the ammonium polyatomic ion. NH4+(aq) NH3(aq) + H+(aq) acidic solution 15. The ammonia molecule, NH3(aq), reacts in an equilibrium reaction with water to increase the [OH−] in aqueous solution. Write an equation to show the dissociation of the ammonia molecule. NH3(aq) + H2O(l) NH4+(aq) + OH−(aq) basic solution 5 ACID NOMENCLATURE 16. (a) What is a binary acid? an acid composed of hydrogen and one other element – the 2nd element will be a nonmetal (b) How are binary acids named? 1 = ALWAYS begin with the word “hydro-“ st 2nd = the ending of the name of the 2nd element is changed to “ic” 17. What are the common binary acids? HF = hydrofluoric acid HCl = hydrochloric acid HBr = hydrobromic acid HI = hydroiodic acid H 2S = hydrosulfuric acid H 2O = hydroxylic acid (A.K.A. – water ) H 3P = hydrophosphoric acid HCN* = hydrocyanic acid *NOTE: this is an exception b/c it is composed of 3 elements 6 18. (a) What is an oxy-acids? an acid composed of a polyatomic ion to which hydrogen has been attached (b) How are oxy-acids named? they are named after the polyatomic ion – but, the ending of the name is changed to “ic” 19. What are the “trendsetter” oxy-acids? Polyatomic Anion NO3─ Polyatomic Name nitrate Acid Name Nitric Acid Chemical Formula HNO3 CO32─ carbonate Carbonic H2CO3 SO42─ sulfate Sulfuric Acid H2SO4 PO43─ phosphate Phosphoric Acid H3PO4 ClO3─ chlorate Chloric Acid HClO3 CrO42─ chromate Chromic Acid H2CrO4 Cr2O72─ dichromate Dichromic Acid H2Cr2O7 MnO4─ permanganate permanganic Acid HMnO4 CNO─ cyanate Cyanic Acid HCNO* *NOTE: this is an exception b/c it is composed of 4 elements 7 20. How can the “Trendsetter” oxy-acids be changed? EXAMPLE Change Made Change in Name Name (+) 1 O atom prefix w/ “per” perchloric HClO4 Chloric HClO3 TRENDSETTER Formula ( ̶ ) 1 Ox atom change “ic” to “ous” chlorous HClO2 ( ̶ ) 2 Ox atoms prefix with “hypo” hypochlorous HClO 21. Practice changing the name or formula of the trendsetters Acid Name a) phosphorous acid Chemical Formula H3PO3 b) sulfurous acid H2SO3 c) nitrous acid HNO2 d) hypophosphorous acid H3PO2 e) carbonous acid H3CO2 f) pernitric acid HNO4 g) hyposulfurous acid H2SO2 h) i) chromous acid Permanganous acid H2CrO3 HMnO3 8 PRACTICE QUESTIONS 22. Identify each of the following compounds as either and acid (A) or a base (B). B a. NaOH A d. H3PO4 A. g. HNO3 B j. Cu(OH)2 A b. HCl B e. Al(OH)3 B h. Ca(OH)2 B k. Ba(OH)2 A c. HCN B f. KOH B i. LiOH A l. HI 23. Write dissociation equations for each of the following acids or bases. Keep in mind whether or not it is a strong or weak electrolyte. 1 of the 8 strong bases Ba(OH)2 (s) → Ba2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) a) barium hydroxide b) nitrous acid HNO3(aq) c) aluminum hydroxide Al(OH)3 (s) a weak acid H+(aq) + NO3─(aq) a weak base Al3+(aq) + 3 OH-(aq) a weak base Pb(OH)4(s) Pb4+(aq) + 4 OH-(aq) d) lead (IV) hydroxide e) calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)2(s) a weak base Ca2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) 1 of the 8 strong bases LiOH (s) → Ba2+(aq) + OH-(aq) f) lithium hydroxide 1 of the 7 strong acids HClO3 (aq) → H+(aq) + ClO3-(aq) g) chloric acid h) copper (II) hydroxide Cu(OH)2 (s) a weak base Cu2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) 9 24. Name each of the following as an acid (A) or a base (B): A a. hydrochloric A e. sulfurous B j. potassium hydroxide B b. calcium hydroxide B f. lithium hydroxide A k. ammonium A c. carbonic B h. aluminum hydroxide B l. ammonia B d. nitric A i. hydrobromic 25. Write chemical formulas for each of the following and classify each as an acid (A) or a base (B): Chemical Formula Acid/ Base Mg(OH)2 B a) magnesium hydroxide HF A b) hydrofluoric HNO3 A c) nitric acid LiOH B d) lithium hydroxide NH4OH B e) ammonium hydroxide H2CrO4 A f) chromic acid Ba(OH)2 B g) barium hydroxide 26. Write the chemical formula for each of the following and then identify each of the following as a strong electrolyte (SE), weak electrolyte (WE), or nonelecrtrolyte (NE). The solubility chart would be helpful! Chemical Formula Electrolyte (a) potassium hydroxide KOH SE (b) sodium carbonate Na2CO3 SE (c) silver chloride AgCl WE (d) dinitrogen pentoxide N2O5 NE 10