Review Sheet Key
advertisement
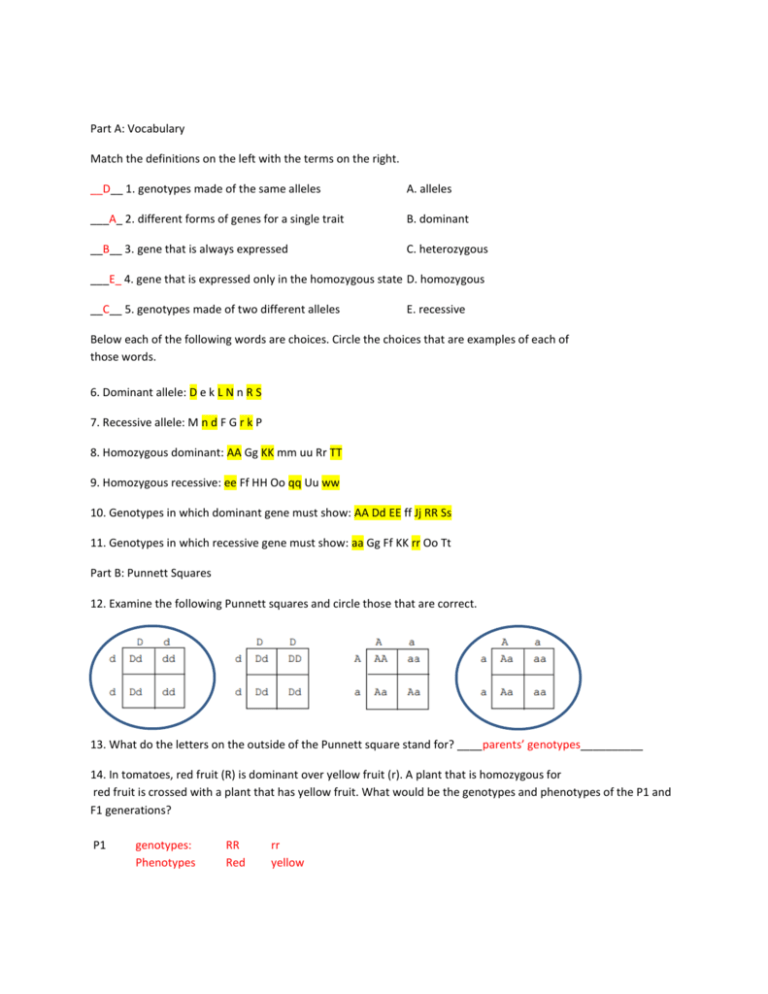
Part A: Vocabulary Match the definitions on the left with the terms on the right. __D__ 1. genotypes made of the same alleles A. alleles ___A_ 2. different forms of genes for a single trait B. dominant __B__ 3. gene that is always expressed C. heterozygous ___E_ 4. gene that is expressed only in the homozygous state D. homozygous __C__ 5. genotypes made of two different alleles E. recessive Below each of the following words are choices. Circle the choices that are examples of each of those words. 6. Dominant allele: D e k L N n R S 7. Recessive allele: M n d F G r k P 8. Homozygous dominant: AA Gg KK mm uu Rr TT 9. Homozygous recessive: ee Ff HH Oo qq Uu ww 10. Genotypes in which dominant gene must show: AA Dd EE ff Jj RR Ss 11. Genotypes in which recessive gene must show: aa Gg Ff KK rr Oo Tt Part B: Punnett Squares 12. Examine the following Punnett squares and circle those that are correct. 13. What do the letters on the outside of the Punnett square stand for? ____parents’ genotypes__________ 14. In tomatoes, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r). A plant that is homozygous for red fruit is crossed with a plant that has yellow fruit. What would be the genotypes and phenotypes of the P1 and F1 generations? P1 genotypes: Phenotypes RR Red rr yellow F1 genotypes: Rr Phenotypes Red Monohybrid Cross 15. A heterozygous, smooth pea pod, plant is crossed with a wrinkled pea pod plant. There are two alleles for pea pod, smooth and wrinkled. Predict the offspring from this cross. a. What is the genotype of the parents? ____Ss x ss__ b. Set up a Punnett square with possible gametes. S s s Ss ss s Ss ss c. Fill in the Punnett square for the resultant offspring. d. What is the predicted genotypic ratio for the offspring ?____0:2:2__________ (homo dom: heter: homo rec) e. What is the predicted phenotypic ratio for the offspring ?____2:2______________ (dominant: recessive) f. If this cross produced 50 seeds how many would you predict to have a wrinkled pod? 50 seeds x .5 = 25 seeds Dihybrid Cross 16. In pea plants, the round seed allele is dominant over the wrinkled seed allele, and the yellow seed allele is dominant over the green seed allele. The genes for seed texture and those for seed color are on different chromosomes. A plant heterozygous for seed texture and seed color is crossed with a plant that is wrinkled and heterozygous for seed color. *R = round, r = wrinkled, Y= yellow, y = green a. Construct a Punnett square for this cross. RY Ry rY ry rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy ry RrYy Rryy rrYy rryy rY RrYY RrYy rrYY rrYy ry RrYy Rryy rrYy rryy b. What is the expected phenotypic ratio for the offspring? _____6:2:6:2_____________________________ (dominant both: dominant in first and recessive in second: recessive in first and dominant in second: recessive in both) Codominant 17. In humans straight hair (ss) and curly hair (cc) are codominant traits, that result in hybrids who have wavy hair (sc). Cross a curly hair female with a wavy haired male. a. Complete a Punnett square for this cross. c c s sc sc c cc cc b. Probability of child having wavy hair? _____50%_____ c. Probability of child having curly hair? _____50%_____ d. Probability of child having straight hair? _____0%_____ Multiple Alleles 18. So far we have studied traits or genes that are coded for by just two alleles. Like in rabbits, there was one allele for brown hair color and one allele for white hair. However, some traits are coded for by more than two alleles. One of these is blood type in humans. This is a violation of Mendel’s Principle of unit characteristics. In humans, there are four types of blood; type A, type B, type AB, and type O. The alleles A and B are codominant to each other and the O allele is recessive to both A and B alleles. So a person with the genotype AA or AO will have A type of blood. a. What possible genotypes will produce B type of blood? _________BB, BO_______________ b. What is the only genotype that will produce O type of blood? ______OO______________ c. What is the only genotype that will produce AB type of blood? ______AB_____________ 19.You are blood type O and you marry a person with blood type AB. a. Complete a Punnett square for this cross. O O A AO AO B BO BO e. List the possible blood types (phenotypes) of your offspring. _type A or type B____ Sex – linked 20. Hemophilia is a sex-linked trait. A person with hemophilia is lacking certain proteins that are necessary for normal blood clotting. Hemophilia is caused by a recessive allele so use “N” for normal and “n” for hemophilia. Since hemophilia is sex-linked, remember a woman will have two alleles (NN or Nn or nn) but a man will have only one allele (N or n). A woman who is heterozygous (a carrier) for hemophilia marries a normal man: a. What are the genotypes of the parents? Woman: XNXn Man: XNY b. Make a Punnett square for the above cross. XN Xn XN XNXN XnXN Y XNY XnY c. What is the probability that a male offspring will have hemophilia? ____50%______ d. What is the probability of having a hemophiliac female offspring? _____0%____ 21. For each term listed below, label whether they are describing mitosis, meiosis, or both. 1. Produces haploid cells Meiosis 2. Occurs in germ cells Meiosis (produces sex cells) 3. Occurs in plant and animal cells Both 4. In humans, produces cells with 23 chromosomes Meiosis 5. Involves cellular division Both 6. DNA is copied once Both 7. Occurs in body (somatic) cells Mitosis 8. Produces 4 cells Meiosis 9. Produces cells that are identical to each other Mitosis 10. Homologous chromosomes line up paired with Meiosis each other 11. Cell divides only once Mitosis 12. Produces diploid cells Mitosis 13. Produces 2 cells Mitosis 14. Has 2 separate divisions Meiosis 15. New cells are different from each other Meiosis 16. In humans, produces cells with 46 chromosomes Mitosis 17. Homologous chromosomes do not line up next to Mitosis each other