Bio 122 Test Review Questions
advertisement
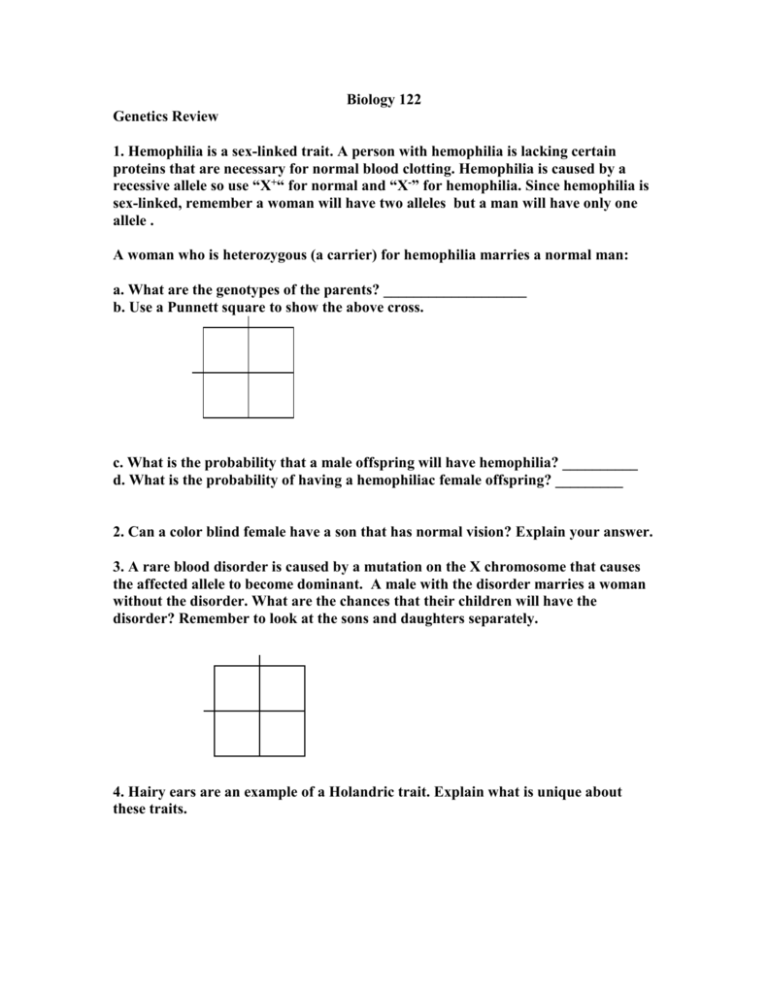
Biology 122 Genetics Review 1. Hemophilia is a sex-linked trait. A person with hemophilia is lacking certain proteins that are necessary for normal blood clotting. Hemophilia is caused by a recessive allele so use “X+“ for normal and “X-” for hemophilia. Since hemophilia is sex-linked, remember a woman will have two alleles but a man will have only one allele . A woman who is heterozygous (a carrier) for hemophilia marries a normal man: a. What are the genotypes of the parents? ___________________ b. Use a Punnett square to show the above cross. c. What is the probability that a male offspring will have hemophilia? __________ d. What is the probability of having a hemophiliac female offspring? _________ 2. Can a color blind female have a son that has normal vision? Explain your answer. 3. A rare blood disorder is caused by a mutation on the X chromosome that causes the affected allele to become dominant. A male with the disorder marries a woman without the disorder. What are the chances that their children will have the disorder? Remember to look at the sons and daughters separately. 4. Hairy ears are an example of a Holandric trait. Explain what is unique about these traits. 5. Fainting sheep is considered a sex influenced trait. Testosterone causes the heterozygous genotype to be expressed as the fainting trait in males, but not in females. “FF” causes fainting in both males and females. “ff”does not in both. A male fainter with the genotype Ff is crossed with a female non-fainter with the genotype Ff. Explain the genotypes and phenotypes of their offspring. 6. In poultry, the dominant alleles for rose comb (R-pp) and pea comb (rrP-), if present together cause walnut comb (R-P-) to form. The recessive alleles (rrpp) produce the rare single comb. What will be the phenotype ratio for the offspring produced from a cross between a walnut combed chicken (RrPp) and a single combed rooster (rrpp). 7. This question deals with epistatic alleles. In mice, black (B_) is dominant to brown (b). A second pairs of alleles (A) affect the expression of the B alleles. If a dominant A allele is present it will allow the B alleles to be expressed. If the A alleles are found in a homozygous recessive genotype, an albino trait will appear. a) Is this an example of recessive epistasis or dominant epistasis? b) Cross two mice with genotypes AaBb. Indicate the phenotype ration of the offspring. 8. Examine the following pedigree chart of color-blindness. In humans, color blindness is caused by a recessive sex-linked allele. On the diagram, label the genotypes of the individuals 1-16 and shade in any carriers. If there is a choice, go with the colorblind/carrier condition.











