11.2 and Dihybrid practice - OG
advertisement

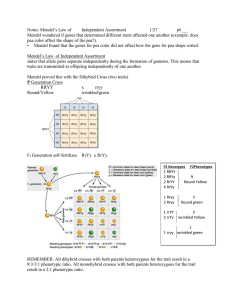
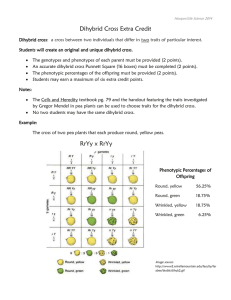
Name ______________________________________________ Period _______________ Use the information in section 11.2 to answer the questions below. 1. What is the Principle of Independent Assortment? What does this mean in your own words? 2. What is the difference between a monohybrid cross and a dihybrid cross? 3. You have mastered monohybrid crosses. Now, you will be challenged to create a dihybrid cross. Fill in the missing genotypes in the dihybrid Punnett Square below. This is a cross between a round yellow plant (RRYY) and a wrinkled green plant (rryy) RY ry RrYy ry ry RY RY RY RrYy RrYy RrYy RrYy ry What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes? RrYy Name ______________________________________________ Period _______________ 4. What results would you get if you crossed two offspring from the previous cross? Create a dihybrid Punnett Square. ____ ____ ____ ____ ___ ___ ___ ___ How many plants are round green? Round yellow? Wrinkled yellow? Wrinkled green? What is the phenotypic ratio for this cross? ______ : ______ : _______ : _______ 5. Here’s a challenge! What would the results be for a cross between a homozygous dominant tall and heterozygous yellow seeded pea plant, and a heterozygous tall and green-seeded pea plant? (Hint: First, figure out the parent’s alleles. Then, determine all possible allele combinations for each parent, and then you can set up your dihybrid Punnett Square.) ____ ____ ____ ___ ___ ___ ___ What are the possible genotypes and corresponding phenotypes? ____



![multiple factor crosses 11-12[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/009912112_1-886981b7474ffcc5888f6913ab3029be-300x300.png)