Ch 35.4 Student notes CD
advertisement

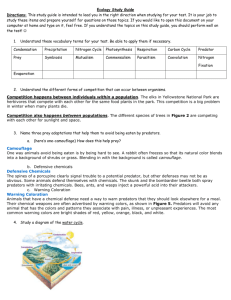
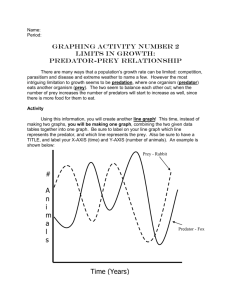
BIOLOGY Name:________________________ Chapter 35: Population and Community Ecology Section Goal: The student will identify causes and possible results of interspecific competition, identify some adaptations of predators and prey and compare and contrast symbiotic relationships. Vocabulary: 1. Interspecific competition2. Competitive exclusion3. Niche4. Predation5. Symbiotic relationship6. Parasitism7. Mutualism8. Commensalism- Concept 35.4-Species interact in biological communities I. Competition Between Species A. Members of a population may compete for the same limited resource B. Within a community, interspecific competition takes place when two or more species rely on the same limited resource C. If two species are so similar in their requirements that the same resource limits both species’ growth it is called competitive exclusion D. Russian biologist, G.F. Gause demonstrated competitive exclusion in the laboratory. He grew two different species of paramecium in separate containers where both thrived. When he grew them in the same container, the two species competed for the limited food available, one survived and the other died. E. A niche includes an organisms living place, its food source, the time of day it is most active and many other factors that are specific to that organism’s way of life II. Predation A. Predation is when one organism eats another B. Eating and avoiding being eaten are important to survival and predators and prey have developed many adaptations 1. Predator adaptations include: being fast and agile, coloring that camouflages, hunting in groups, acute sense to find prey and having claws, teeth, fangs and stingers to help catch prey 2. Prey adaptations include: retreating or fleeing from predators, camouflage, defensive coloring, mimicry, secreting poisonous chemicals, having spines and thorns III. Symbiotic Relationships A. A symbiotic relationship is when two species live in or on one another B. There are three main types of symbiotic relationships 1. Parasitism- A parasite gets it’s food at the expense of another organism, i.e. mosquitos and humans 2. Mutualsim- Both organism benefit from the relationship, i.e. E.Coli and humans 3. Commensualism- One organism benefits and the other is neither hurt nor helped, i.e. sharks and remoras Lesson Reflection: Complete online activity 35.4 at https://www.pearsonsuccessnet.com. Review of graphing: Interpreting Ecological Data handout Lesson Assessment: 1. How did Gause’s experiment with Paramecium demonstrate competitive exclusion? 2. Describe two methods predators use to help them capture their prey and two methods prey use to help them avoid being eaten. 3. Define and give an example of each of the three types of symbiotic relationships. Summary of Key concepts: Complete the Summary of Key Concepts for34.4 and turn into the box. Technology/Application/Connection to real-world: Predator/Prey Activity (fish & eagle) PBS: Survival of the Fastest: Predators and Prey on the African Savanna activities. Complete: Anatomy of a Cheetah, Video Guide (Cheetah vs. Gazelle & Lion vs. Wildebeest) and “Toki’s Survival Challenge” game. You will need to access my website through the Plain Local website in order to complete this activity.