Study Guide Ecology 1
advertisement
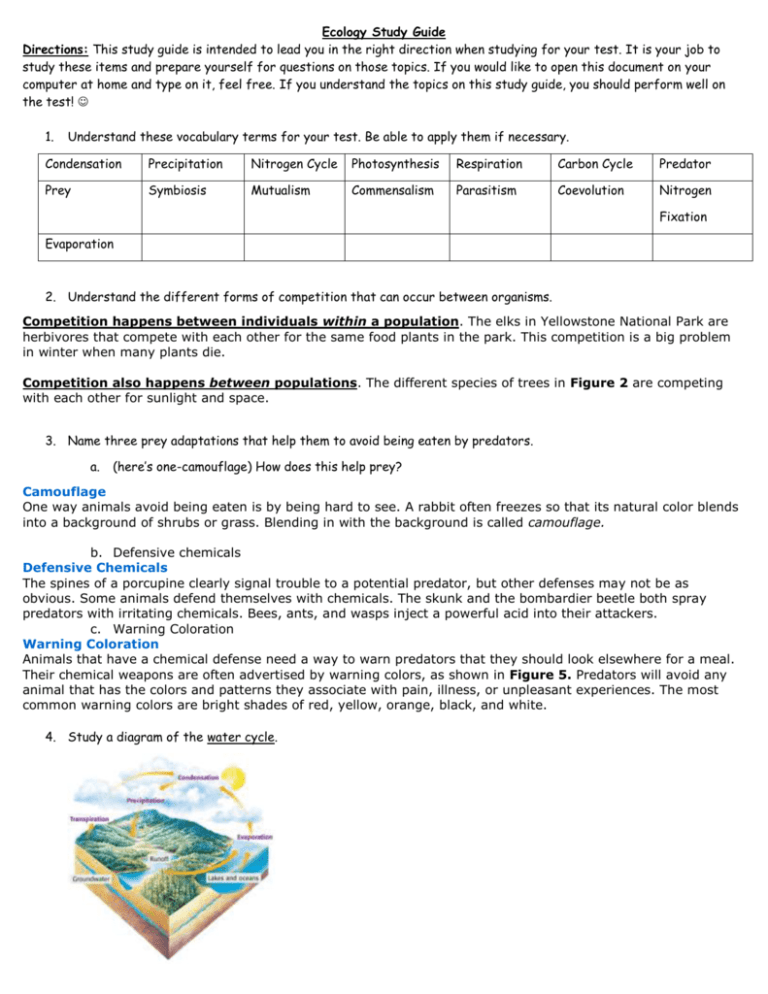
Ecology Study Guide Directions: This study guide is intended to lead you in the right direction when studying for your test. It is your job to study these items and prepare yourself for questions on those topics. If you would like to open this document on your computer at home and type on it, feel free. If you understand the topics on this study guide, you should perform well on the test! 1. Understand these vocabulary terms for your test. Be able to apply them if necessary. Condensation Precipitation Nitrogen Cycle Photosynthesis Respiration Carbon Cycle Predator Prey Symbiosis Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Coevolution Nitrogen Fixation Evaporation 2. Understand the different forms of competition that can occur between organisms. Competition happens between individuals within a population. The elks in Yellowstone National Park are herbivores that compete with each other for the same food plants in the park. This competition is a big problem in winter when many plants die. Competition also happens between populations. The different species of trees in Figure 2 are competing with each other for sunlight and space. 3. Name three prey adaptations that help them to avoid being eaten by predators. a. (here’s one-camouflage) How does this help prey? Camouflage One way animals avoid being eaten is by being hard to see. A rabbit often freezes so that its natural color blends into a background of shrubs or grass. Blending in with the background is called camouflage. b. Defensive chemicals Defensive Chemicals The spines of a porcupine clearly signal trouble to a potential predator, but other defenses may not be as obvious. Some animals defend themselves with chemicals. The skunk and the bombardier beetle both spray predators with irritating chemicals. Bees, ants, and wasps inject a powerful acid into their attackers. c. Warning Coloration Warning Coloration Animals that have a chemical defense need a way to warn predators that they should look elsewhere for a meal. Their chemical weapons are often advertised by warning colors, as shown in Figure 5. Predators will avoid any animal that has the colors and patterns they associate with pain, illness, or unpleasant experiences. The most common warning colors are bright shades of red, yellow, orange, black, and white. 4. Study a diagram of the water cycle. a. Explain the processes of condensation, precipitation, transpiration, and evaporation. How Water Moves During evaporation, the sun’s heat causes water to change from liquid to vapor. In the process of condensation, the water vapor cools and returns to a liquid state. The water that falls from the atmosphere to the land and oceans is precipitation; plants release a large amount of water vapor in a process called transpiration b. Be able to label these on the diagram. 5. Study a diagram of the carbon cycle. a. Explain the processes of respiration and photosynthesis. i. Which process releases carbon into the soil? ii. Which processes release it into the atmosphere? iii. Which process removes carbon from the atmosphere? 6. Study a diagram of the nitrogen cycle. a. Explain the process of nitrogen fixation. i. Who or what performs this process? ii. How do animals get the nitrogen they need? 7. Be able to identify symbiotic relationships based on a given scenario. A symbiotic relationship in which both organisms benefit is called mutualism. A symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected is called commensalism. A symbiotic association in which one organism benefits while the other is harmed is called parasitism.









