File
advertisement

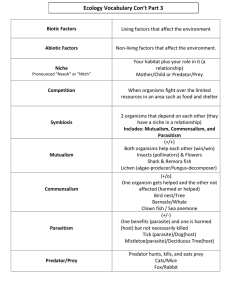
Food Chains and webs Web vs. Chain A food web shows the interconnectivity of all organisms in a given ecosystem. It can flow in more than one direction. A food chain is a single energy pathway that can only flow in one direction. FOOD WEBS Typically, food webs go like this: Record this example in your notes. FOOD CHAINS AND WEBS Let’s make our own food web! Symbiosis TN Standard: I CAN….analyze the environments and the interdependence among organisms found in the world’s major biomes. Symbiosis A relationship in which two different organisms live in close association with each other. Mutualism Commensalism Parasitism Mutualism A symbiotic relationship between two species in which both species benefit. Commensalism A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected. Parasitism A relationship between two species in which one species, the parasite, benefits from the other species, the host, which is harmed. Can you identify these symbiotic relationships ? Can you identify these symbiotic relationships? Predator-Prey What We Know About Predator and Prey Relationships? Predator eats the prey Prey is what is eaten The prey develops defense mechanisms to prevent being eaten Putting it together Compare and Contrast a Food Chain Vs. a Food Web. List and Describe all symbiotic relationships. If you finished early, work on your article response. (Due Friday)