Metric Measurement Week 2 9.15-19.14 Review Discussion What
advertisement

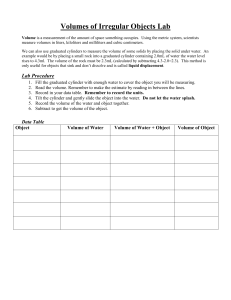
Metric Measurement Week 2 9.15-19.14 Review Discussion What system of measurement does the scientific community use? o SI or Metric System Why do they use the metric system? o Most countries utilize it. o Easier conversions What is our base unit for length? What is our base unit for volume? What is our base unit for mass? What are the prefixes generally used in the metric system? o Kilo, Hecto, Deca, Base, Deci, Centi, Milli What do the prefixes mean? Why do we need them? What do we use to measure length with? o Meter Stick What do we use to measure volume with? o Graduated cylinder What do we use to measure mass with? o Triple Beam Balance WDWL This is a Triple Beam Balance. Parts of a Triple Beam Balance Set Up/Demonstration o Move all three sliders so that they read ‘zero’. o Make sure that there is nothing on the pan and that it is clean. o Check to see if the balance reads zero. o Your balance isn’t reading zero so you need to turn the thumbscrew to adjust the balance until it reads zero o Moving Sliders o Begin with the largest. When moving a slider causes the balance to tip, move the slider back to the previous position. o Move the next slider until it tips the balance. Place is in the previous position. o Move the final slider until the balance reads zero. Reading the sliders begin at the largest and work forward to you (smallest). Assignment: Reading a triple beam balance1 Metric Measurement Week 2 9/16/14 Discussion Questions: What are the parts of a Triple Beam Balance? o Pan: where object is sat. o Thumbscrew: adjust arm for calibration o Sliders: used to determine the mass of the object o Zero mark: used to determine if a scale is calibrated and if we have the correct mass How do we set up a Triple Beam Balance o Move all three sliders so that they read ‘zero’. Why do we do this? o Make sure that there is nothing on the pan and that it is clean. Why do we do this? o Your balance isn’t reading zero so you need to turn the thumbscrew to adjust the balance until it reads zero Why do we do this? How do we move the sliders o Begin with the largest. When moving a slider causes the balance to tip, move the slider back to the previous position. Where is the largest slider? How big are these units? Why do we start with this one? o Move the next slider until it tips the balance. Place is in the previous position. o Move the final slider until the balance reads zero. Reading the sliders begin at the largest and work forward to you (smallest). Practice: Have students practice finding the mass of object for 15 min. WDWL: Volume/Length Volume: What is volume? o The amount of space an object takes up What is our base unit for volume? o liter What piece of equipment do we use to find an objects volume? o Graduated Cylinder How do we calculate volume? o Length x width x height o EX: 6 X 6 X 6 o EX: 12 x 5 x 6 Most of the time we use volume to measure liquid amounts. Which if we know the capacity of a container we can figure out the volume of the liquid. o Meniscus: Liquids tend to create a bowl shape when placed in a container this is called a meniscus. In order to get an accurate reading we “read” a volume by measuring to the lowest level of the meniscus. Well not everything is a liquid and fits in a nice container, or a perfect regular shape. So then how can we measure its volume if its irregular? o Volume by Displacement Put water into a graduated cylinder, 10ml minimum, but do not fill it up all the day. Write down initial volume of the water in the cylinder Carefully place object into the cylinder being sure not to splash water out. Get final volume of water. Do the math, Final Volume – initial volume = Volume of object by displacement. Metric Measurement 2 9/17/14 Review Discussion Volume: What is volume? o The amount of space an object takes up What is our base unit for volume? o liter What piece of equipment do we use to find an objects volume? o Graduated Cylinder How do we calculate volume of a regular shape? o Length x width x height o EX: 7 X 7 X 7 o EX: 10 x 5 x 8 Most of the time we use volume to measure liquid amounts. Which if we know the capacity of a container we can figure out the volume of the liquid. o What is a meniscus? o Meniscus: Liquids tend to create a bowl shape when placed in a container this is called a meniscus. In order to get an accurate reading we “read” a volume by measuring to the lowest level of the meniscus. Demonstration: Measuring with meniscus in graduated cylinder, Measuring Irregular solids by displacement WDWL : Volume/Length cont. o o Well not everything is a liquid and fits in a nice container, or a perfect regular shape. So then how can we measure its volume if its irregular like a rock? o Volume by Displacement Put water into a graduated cylinder, 10ml minimum, but do not fill it up all the way. Write down initial volume of the water in the cylinder Carefully place object into the cylinder being sure not to splash water out. Get final volume of water. Do the math, Final Volume – initial volume = Volume of object by displacement. Measuring Length: o Measured using meter stick o The side with smallest measurement is the side we will use o Never measure with the very end of meter stick because it can be damaged. Assignment: Volume measurement1