Index3
advertisement

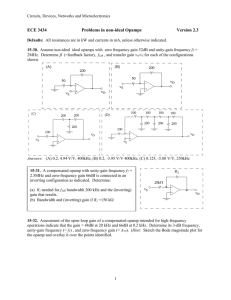
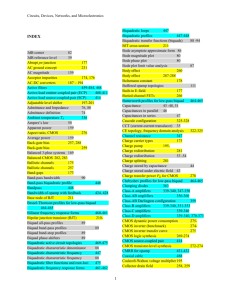
Circuits, Devices, Networks, and Microelectronics INDEX Power amplifier power flow 335 Power dissipated in the circuit, PD 335 -338 Efficiency in power amplifiers 335 Thermal resistance 336 Maximum rated junction temperature TJ(max) 336 Junction temperature TJ 336 Ambient temperature TA 336 Mil-spec requirements 337 Contact thermal resistance 337 Heat sink resistance 337 Maximum power hyperbola 338 De-rated power 338, 339 Duty cycle classification of power amplifiers 339, 340 Class-A amplifiers 339-340, 347-350 Class-B amplifiers 339-340, 351-353 Class-C amplifiers 339-340 Class-D amplifiers 339-340, 370-373 Power transistors 341-342, 344-347 pin junction 342-343 Power BJT 344-346 Drift region 344 Quasi-saturation 344-346 Power MOSFET 346-347 Velocity saturation 347 Channel resistance 347 HEXFETs 347 Distortion 353-354 Cross-over distortion 355 Class-AB amplifiers 356Thermal runaway 357 Darlington pair 358 Super-beta transistor 358 VBE multiplier 359 Class-AB Darlington configuration 359 Instantaneous power dissipation 361 Clamping diodes 363 Snubber 363 Short-circuit protection 363 1 Circuits, Devices, Networks, and Microelectronics Fold-over current limiting 363-365 Power opamps 365-369 Power bridge 367-369 Pulse-width modulation 370 Double-diffused structure 346 Ideal switch 377 Down converter 377-383 Complementary switches 377 Time-averaged sinusoidal power 340 Series switch 379 Shunt switch 379 Time-averaging 378-379 Ripple in DC-DC converters 379, 382-383, 386Duty cycle of series switch 379 Inductive complementary switching 380 Direct down-converter 380 Direct up-converter 383-387 DC-DC indirect up-down converter 388 Turn-on and turn-0ff times in switches 390 Power dissipated during transition 389-390 Differential amplifier 395 Differential coupled pair 395 Current steering 395-396 Emitter-coupled pair 396-401 Single-ended ECP 400 ECP half 401 Common-mode gain 401 Common-mode rejection ratio (CMRR) 401, 405, 407, 413 Stiff current sources 401-404 Simple current mirror 402 Wilson current mirror 403 ECP with Darlington-pair inputs 404 Active-load emitter-coupled pair (ECP) 408-411 Source-coupled pair (SCP) 411-414 CMOS source-coupled pair 414 Active-load source-coupled-pair (SCP) 414 Nullator-norator 419, 347 Common-mode rejection 419,431 Slew-rate 419,433-434 Feedback factor for opamp 419 Feedback for opamp with finite gain 419-422 Non-inverting topology 419-421 Inverting topology 419-422 Virtual connection 422 2 Circuits, Devices, Networks, and Microelectronics Zero frequency gain of opamp 423 Unity-gain frequency of opamp 423 Compensation of opamp to a STC response 422 Gain-bandwidth product (GB) of opamp 423 Bandwidth of opamp with feedback 424, 428 Effect of feedback on opamp Rin 424-425 Equivalent input impedance Zin 425-428 Effect of feedback on opamp Rout 428-429 Equivalent output impedance Zout 429-430 Equivalent input pseudo-capacitance Ceq 427 Equivalent output pseudo-inductance Leq 428 CMRR for opamp 431-432 Compensation capacitance of opamp 433 Opamp macromodels 434-440 Macromodel for LM342 opamp 435-436 Macromodel for LF411 opamp 436-437 Maximum power bandwidth 433 Instrumentation amplifier 432 Feedback, generic 443 Feedback, negative 443 Loop gain 443 Nyquist plot 443 Stability of circuits with feedback 444 Phase margin (PM) 444 Gain margin (GM) 444 Unit circle 444 Gain stabilization 445 Desensitivity factor 446-447 Feedback effect on I/O impedances 446 Sampling and insertion in feedback 446 Biquadratic loops 447 Biquadratic profiles 447-448 Low-pass biquadratic profile 448 Band-pass biquadratic profile 448 Biquadratic characteristic frequency 447 Bandpass 448 Gain-peaking (GP) 448, 455 Maximally-flat biquad profile 449 Gain-peaking frequency 452-453 Pulse overshoot (OS) 456 Root-loci for biquadratic functions 456 Gain-peaking and phase margin (PM) 457 Active filters 459-484, 468 Bilinear frequency response forms 460-461 3 Circuits, Devices, Networks, and Microelectronics Biquadratic frequency response forms 461-462 Butterworth profiles for low-pass biquad 464-465 Chebyshev profiles for low-pass biquad 464-465 Bessel-Thomson profiles for low-pass biquad 464-465 Ripple in the stop-band 465 Ripple in the pass-band 465 Normalized forms 465 Frequency rescaling 465-468 Rescaling frequency 467 RC rescaling 467-468 RLC rescaling 468 Impedance-magnitude rescaling 468 Biquadratic active circuit topologies 469-475 Sallen-Key tunable-Q topology 469-470 Sallen-Key, tapering factor 470 Sallen-Key, Saraga low-sensitivity design 471 Two-integrator loop 471 State-variable filters 471-472 Tow-Thomas biquad 472 Ring-of three biquad 472 Biquadratic filter functions and root-loci 475 Fourth-order Butterworth profile using Sallen-Key 476 Fourth-order Chebyshev profile using root-loci 477 Ripple factor of Chebyshev profile 477 Fourth-order Chebyshev profile using Sallen-Key 477 Doubly-terminated RLC ladders 477-478 RLC:CRD transformation 480-481 Frequency-dependent negative resistance (FDNR) 480-481 Generalized Impedance Converter (GIC) 481-482 Doubly-terminated RLC ladder and 5th-order Chebyshev 482-484 th RLC:CRD transformation and 5 -order Chebyshev 482-484 Equal-capacitance realization 483 Fleige topology 481 UHF regime 487 Distributed parasitic reactance 487 Transmission lines 487-489 Coaxial cable 488 Transmission line impedance Z0 488 Reflection coefficient 0 489, 490 Reflection coefficient 489, 490 Propagation constant 490 Phase velocity 490 Speed of light 490 Free-space wavelength 490 4 Circuits, Devices, Networks, and Microelectronics Standing-wave ratio (SWR) 492 Voltage standing-wave ratio (VSWR) 492 Matched load 490,493 Line phase 493 Quarter-wave transformer 494 Microstrip lines 494 Normalized impedance 495 Smith chart 495-499 Z-Smith chart 495-496 YZ-Smith chart 497 Reactance paths 498-499 Susceptance paths 498-499 Nomograph 496, 498 Dynamic range 501, 522 Fugacity 501 Thermal noise voltage 501-502 Thermal noise current 501-502 Johnson-Nyquist noise 502 Johnson noise 503 Thermal noise 503 White (full-spectrum) noise 503 Nyquist formula 503 Noise bandwidth 502,504 Signal to noise ratio 504 Noise factor 505 Noise temperature 505 Noise floor 506 Minimum detectible signal 506 dBW 506 dBm 506 Noise figure 506 Cascaded stages and noise 507-508 Noise in amplifiers 510 Shot noise 510-511, 513-5-14 Noise spectral density (NSD) 510 Pink noise 511 1/f noise 511 Optimum source resistance 512 Base-spreading resistance 513 Optimized collector current IC 516 Noise nomenclature in pspice 518-520 Optimization of noise factor 520 Intermodulation distortion 521 Cubic distortion 521 5 Circuits, Devices, Networks, and Microelectronics Two-tone intercept level 522 6