LAB-4 Wireless Networks Course Instructor: Dr.Amina Saleem Lab

LAB-4
Wireless Networks
Course Instructor: Dr.Amina Saleem
Lab Conducted by Miss Moonerah Al-Eidi
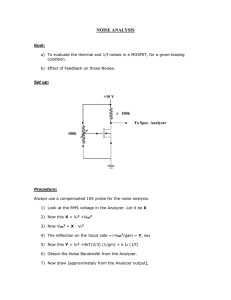
Question No 1:
The room temperature is usually taken to be 𝑇 = 17 𝑜
𝐶 or 290𝐾 . At this temperature find the thermal noise power density.
Solution:
𝑵 𝒐=
𝑲𝑻 (
𝑾𝒂𝒕𝒕𝒔
𝑯𝒛
)
Where 𝑲 = 𝟏. 𝟑𝟖𝟏𝟎
−𝟐𝟑
is the Boltzman constant. And 𝑵 𝒐
is the thermal noise power density per Hertz or bandwidth.
𝑵 𝒐=
𝑲𝑻 (
𝑾𝒂𝒕𝒕𝒔
𝑯𝒛
) = (𝟏. 𝟑𝟖 × 𝟏𝟎 −𝟐𝟑 × 𝟐𝟗𝟎 = 𝟒 × 𝟏𝟎 −𝟐𝟏 (
𝑾𝒂𝒕𝒕𝒔
𝑯𝒛
) = −𝟐𝟎𝟒𝒅𝑩𝑾/𝑯𝒛
The expression for 𝒅𝑩
𝑾
= 𝟏𝟎𝒍𝒐𝒈
𝟏𝟎
(𝑷𝒐𝒘𝒆𝒓 𝒊𝒏 𝒘𝒂𝒕𝒕𝒔/𝟏𝑾𝒂𝒕𝒕) .
𝒅𝑩
𝑾
is an absolute level of power relative to 1W which selected as a reference and defined to be 𝟎𝒅𝑩 𝒘
The thermal noise is called white noise as it is constant over the entire bandwidth. So given a receiver with the above noise temperature and a 10MHz bandwidth, the thermal noise at the receiver’s output is given by:
𝑵 𝒐
= 𝑲𝑻𝑩
𝑵 𝒅𝑩
= −𝟐𝟐𝟖. 𝟔 + 𝟏𝟎𝒍𝒐𝒈(𝟐𝟗𝟒) + 𝟏𝟎𝒍𝒐𝒈𝟏𝟎 𝟕
𝑵 = −𝟏𝟑𝟑. 𝟗𝒅𝑩𝑾
Question No 2:
Consider a voice channel being used via modem to transmit digital data. Assuming a bandwidth of 3100 Hz. Then the Nyquist capacity is given by the following considering M=2
𝑪 = 𝟐𝑩 = 𝟔𝟐𝟎𝟎𝒃𝒑𝒔
If we use M-Ary Signalling where the total number of levels are M=8 then the channel capacity is eaual to 18600 b/s over a bandwidth of 3100Hz.
𝑪 = 𝟔𝟐𝟎𝟎 × 𝟑 = 𝟏𝟖𝟔𝟎𝟎 𝒃𝒊𝒕𝒔/𝒔𝒆𝒄𝒐𝒏𝒅
Question No 3
Prove the following expression for the Signal energy/bit to Noise power per Hz or the ratio
𝑬 𝒃
𝑵 𝒐
The relationship between the
𝑬 𝒃
𝑵 𝒐
and the SNR can be represented as
The relationship between the
𝑬 𝒃
𝑵 𝒐
and the spectral efficiency can be found out as
Question No 4:
Given
𝑬 𝒃
𝑵 𝒐
= 8.4𝑑𝐵 is required to achieve a bit error rate of 10
−4
.If the effective noise temperature is 290𝑘 and the data rate is 2400bps, what received signal is required.
8.4 = 𝑆(𝑑𝐵𝑊) − 10 log(2400) + 228.6𝑑𝐵𝑊 − 10𝑙𝑜𝑔290 = −161.8𝑑𝐵𝑊
Question No 5:
Find the minimum 𝑬 𝒃
/𝑵 𝒐
required to achieve a spectral efficiency of 6bps/Hz.
𝑬 𝒃
𝑵 𝒐
=
𝟔(𝟐 𝟔
𝟏
− 𝟏)
= 𝟏𝟎. 𝟓 = 𝟏𝟎. 𝟐𝟏𝒅𝑩
Question No 6:
If the maximum distance between two antennas for LOS transmission is 41Km. Find the length of the transmitting antenna if the length of the receiving antenna is 10 m.
𝟒𝟏 = 𝟑. 𝟓𝟕(√𝑲𝒉
𝟏
+ √𝟒/𝟑 × 𝟏𝟎) 𝒉
𝟏
= 𝟒𝟔. 𝟐𝒎
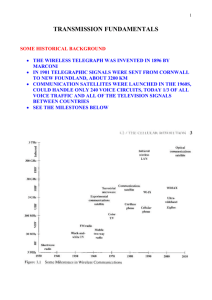
Question No 7:
Following Figure gives us the relationship between the free space loss with distance and the frequency. What can you interpret between the relationship of the loss with increasing distance and increasing frequencies.
Solution:
We can see from the following curve, that the free space loss increases with increasing distance from the transmitter and it is higher for higher frequencies.