20141023153778
advertisement

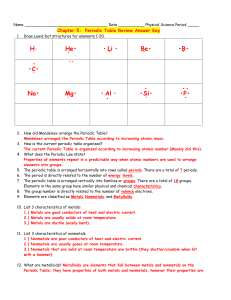
Chapter 5 Study Guide Section 1 Vocabulary: Periodic Table Lavoisier- grouped known elements into categories: m,nm,g,earths How many elements had been discovered up until 1750-17 Mendeleev (1860) o # of known elements at his time-63 o what inspired his approach to the periodic table-solitaire o made a “deck of cards” o what patterns did he notice-similar properties in same column o what was his final arrangement of the periodic table-rows increasing mass, organized by properties o what was missing in his table-undiscovered elements o how did he predict undiscovered elements-used properties of elements located near blanks o was he the first to make a periodic table-no o what does the placement of the elements reveal links between-atomic structure of elements & their properties o how were his predictions-accurate o (section) he developed his table the discovery of what-gallium Section 2 Vocabulary: period, group, periodic law, atomic mass unit (amu), metals, transition metals, nonmetals, metalloids How are sounds of musical notes related to the periodic table-periodic pattern What does octa mean-8 How is the modern periodic table arranged-increasing atomic number How are elements related in groups-similar properties Why is the gram measurement unit not useful for element mass-atom extremely small What is the convenient way to compare masses of atoms-one isotope to serve as standard Know the different ways to classify elements: o 1st- based on their state at room temperature (know their location) solids liquids gases nd o 2 - naturally occurring or not which ones do not occur naturally-93 and higher o 3rd- based on their general properties metals nonmetals metalloids Metals: location, know characteristics (ex: what is ductile), where are the transition metals (what is one property that many of the transition metals share?) Nonmetals: location, know characteristics What is the most reactive nonmetal-fluorine Metalloids: where are they, characteristics How do elements vary across a period-become less metallic, atomic number increase by 1 Most reactive metals are where-left side (alkali metals) Most reactive nonmetals are where-right (halogen group) Section 3- Representative Groups Vocabulary: valence electron, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases Why is Hydrogen on the left side of the periodic table-bc of electron configuration, not properties What is the difference between electrons and valence electrons electron is total #, valence electron is # of electrons in highest occupied Energy level How does the number of valence electrons vary across a period-increases from L to R Know the families (groups) o Alkali Metals location # of valence electrons1 reactivityhigh why are sodium and potassium stored under oil to keep from reacting with air o Alkaline Earth Metals Location # of valence electrons2 Magnesium Key role in photosynthesis Mixture of Mg and other metals is strong as steel, but lighter Calcium Bones need it Calcium carbonate: Ca, C, O Chalk, limestone, coral, pearls o Boron Family Location # of valence electrons3 Aluminum is the most abundant metal in Earth’s crust o Carbon Family Location # of valence electrons4 Silicon is the 2nd most abundant element in Earth’s crust o Nitrogen Family o o o o o Location # of valence electrons5 nitrogen and phosphorus are used in what fertilizer Oxygen Family Location # of valence electrons6 Oxygen is the most abundant element in Earth’s crust; ozone Sulfur: one of the first elements discovered Halogens Location # of valence electrons7 reactivity (high or low); which is most reactive-high, F Noble Gases Location # of valence electrons, what is the exception 8, He 2 characteristics Lanthanide Series Location Actinide Series Location