Carbonyl Group - e-CTLT
advertisement

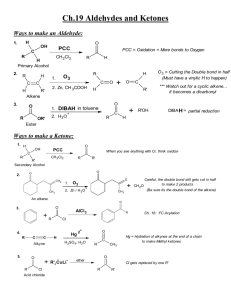
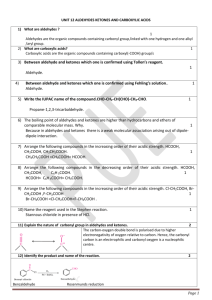
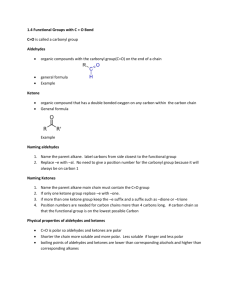
Carbonyl Group- The functional unit is called carbonyl group. C=O present in the organic compound ALDEHYDE- They have the functional group ---CHO. KETONES- Have the functional group R---CO----R’. ACYL HALIDES- They are derived by replacing the hydroxyl groupof a carboxylic acid by a halogen atom.-R—CO—Cl. ACID ANHYDRIDES- They are obtained by the loss of water from two molecules of an acid. (RCO)2O. ESTERS- contains RCOOR group having pleasant smell. Preparation of aldehydes and ketones----1- From Alcohols- K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 RCH2OH R’ K2Cr2O7/H2SO4 RCHOH RCHO R’ R-C=O 2- From AlkynesHgSO4/H2SO4 CHΞCH H2O CH3-CH=O Chemical ReactionsAldehydes and ketones undergo NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION reactions with complete transfer of electron to the oxygen atom. Nu OH+ OH Nu C=O C C CLEMMENSEN REDUCTION---- Amalgated Zinc and conc. HCL reduces aldehydes and ketones to hydrocarbons. Zn/HCl CH3CHO CH3-CH3 + H2O WOLFF-KISHNER REDUCTION--- In presence of Hydrazine and heating with KOH N2H4 KOH GLYCOL R-CHO R-CH=N-NH2 R-CH3 + N2 ALDOL CONDENSATION----- Aldehydes and ketones having atleast one alpha hydrogen undergo a reaction in presence of dil alkali to form β-hydroxy ketone. Dil NaOH CH3-CHO OH heat CH3-CH-CH2-CHO CH3-CH=CH-CHO 3-hydroxy butanal But-2-enal CANNIZARO REACTION-----If no alpha hydrogen is present in aldehyde undergo disproportionation. Conc. KOH 2 HCHO CH3OH + HCOONa TEST TO DISTINGUISH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES 1. Tollens reagent test----Tollens reagent ( ammonical siver nitrate) reduces aldehyde to form silver mirror. RCHO + 2[Ag(NH3)2]+ +3 OH- RCOO- + 2 Ag + 2 H2O +4 NH3 2. Fehlings Test--- When aldehydes are warmed with Fehlings solution a red ppt is formed. CH3CHO + 2 Cu(OH)2 + 2 NaOH CH3COONa + Cu2O + 3 H2O CARBOXYLIC ACIDS--- “e” of the alkane is replaced by “ oic acid” CH3CH2COOH -- Propanoic acid. COOH ------- Benzoic acid PREPARATION--1. From primary alcohols and aldehydes— Alk KMnO4/ H2O RCH2OH RCOOH 2. From Grignard reagent--Dry ether/H3O+ R-Mg-X + O=C=O RCOOH Chemical properties—Carboxylic acid is stronger acid than the phenol because the COO- ion has two equivalent resonating structures than the phenoxide ion which has five non equivalent structure. O R-C-O- Oand R-C=O Presence of electron withdrawing group increases the acidic strength and presence of electron donating group decreases the strength. CCl3COOH >CHCl2COOH >ClCH2COOH REACTIONS--1. Esterification – RCOOH + R’OH H+ RCOOR’ + H2O 2.Reaction with Ammonia----With ammonia they give ammonium salts which on further heating give amides. CH3COOH + NH3 CH3COONH4 heat CH3COONH2 Acetamide 3.HALOGENATION---Carboxylic acids having an alpha hydrogen are halogenated at the alpha position on treating with halogen in presence of red phosphorus. X2/ red phosphorus R-CH2-COOH R-CH-COOH H2O acid) X (α-halocarboxylic