STUDY GUIDE Processes That Change the Earth:
advertisement

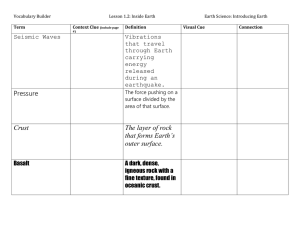
STUDY GUIDE Processes That Change the Earth: Unit C- Chapter 1 in the Science Book If you know these things you will do well on the test. They may be restated in the test or asked differently, but the concepts will be the same. Terms to know: Continental drift- Theory of how continents move over the surface of the earth. Pangea- the Supercontinent of millions of years ago. Godwana and Laurasia- the two smaller continents formed when Pangea split apart. Volcano- a place in earth’s crust where magma from the mantle can rise up out of the surface of the earth. Fault- place where pieces of the crust move Fossils- remains or traces of past life found in the rocks of the crust. Magma- molten or melted rock in the mantle of the earth. Lava- is magma that is now out of the earth. Earthquake- when two plates pass each other they can slip and cause the ground to shake from the release of energy. Landforms- physical features of earth’s surface- like mountains, peninsulas, islands, lakes Weathering- the process of breaking up rocks into sand, silt, clay and sediment Erosion- moving sediment, rocks, clay, and sand from one place to another. Deposition- depositing the sediment in a new location Mass movement- caused by gravity, the downhill movement of rock and soil, a mudslide Plate- a piece of the earth’s crust Crust- the outer most layer of the earth- it is very thin like an eggshell Mantle- below the crust, it is made of melted rock Core- the center of the earth, it is made of solid iron Concepts: Magma, Lava, and volcanoes: How are the highest mountains formed? How do earthquakes happen? The 3 layers of the earth. Surface processes that change landforms: weathering, erosion, and deposition 4 agents of erosion and weathering: wind, water, ice, gravity Theory of Continental Drift: Pangea, Godwana, and Laurasia Evidence of continental drift: similar findings of fossils, and rock layers in different places.