Match The description in column A to the term in column B column A
advertisement

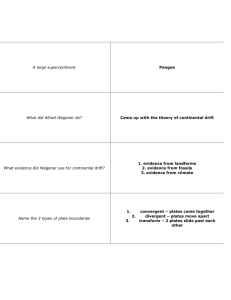
Match The description in column A to the term in column B column A 1. column B Fastest kind of seismic wave (A) Convection (B) Compaction wave 2. Structure a scientist builds to represent something (C) Trench (D) Surface wave 3. Process that consumes ocean crust where two plates meet (E) 4. 5. Bending of a wave due to changes in its velocity Waves that can't travel through liquids Subduction (F) R wave (G) model (H) shear waves (I) Refraction 6. The oceanic crust is __________ than continental crust. A. Thinner B. Less dense C. Smaller in area D. Thicker 7. The Earth's crust and mantle: A. Do not touch B. Have the same chemical composition C. Have different densities D. Have the same thickness 8. The part of the Earth that is made of high-temperature liquid iron is called the: A. Mantle B. inner core C. Outer core D. lithosphere E. asthenosphere 9. Mantle ____________ plays an important role in moving Earth's lithospheric plates A. Conduction B. convection C. refraction D. liquefaction 10. New crust is formed and spreads apart at: A. subduction zones b. convergent boundaries C. transform boundaries D. divergent boundaries 11. One plate slides past another horizontally at: A. subduction zones b. convergent boundaries C. transform boundaries D. divergent boundaries 12. What name did Alfred Wegener give to his theory of horizontal movement of the Earth's crust? A. Plate tectonics B. Continental Drift C. isostasy D. Sea-floor spreading 13. What name did Wegener give to his proposed single supercontinent? A. panthalassa B. Eurasia C. Gondwanaland D. Pangea 14. Which of the following kinds of evidence did Wegener use to support his theory? A. Distributions of fossil plants and animals in the ocean B. Geographic fit of continents C. Patterns of earthquakes and volcanoes around the ring of fire D. All of the above 15. Why did most scientists of the 1920's reject Wegener's theory? A. The Earth was thought to be too young for such movements. B. The concentration of continents in the Northern Hemisphere C. Wegener was not a geologist by training , so his ideas were ignored D. Lack of a mechanism that could move the continents 16. The San Andreas Fault in Southern California is an example of a: A. convergent boundary B. continental plates and the lithosphere C. transform boundary D. divergent boundary 17. What is the term used for molten rock within the Earth? A. magma B. lava C. granite D. pumice 18. The plates are moving about how fast? A. 5 meters a year B. 5 kilometers a year C. About the speed your fingernail grows D. About the speed a fish can swim 19. Most earthquakes occur where? A. at the poles B. very deep within the Earth (> 900 KM deep) C. in the middle of plates D. At plate boundaries 20. If you felt a compaction wave but not a shear wave, the reason for this is probably what? A. The shear wave ran into liquid B. There never was a shear wave created C. The shear wave ran into very dense rock D. The shear wave refracted Match the location on the map to its name 21. Location 1 is: (A) trench 22. Location 2 is : (B) mantle 23. Location 3 is : (C) volcanic arc 24. Location 4 is : (D) oceanic crust 25. Location 5 is : (E) continental crust 26. Location 6 is : (F) subduction zone 27. Continental drift is caused by what? A. subduction B. convection currents C. transform boundaries D. Pangea 28. Where does a subduction zone take place? A. divergent boundary C. can happen at any type of boundary B. convergent boundary D. transform boundary 29. What is the largest layer? A. core B. crust C. outer core D. mantle E. inner core Match the fact with the layer 30. crust (A) is solid iron 31. lithosphere (B) convection currents are here 32. mantle (C) the least dense layer 33. inner core (D) made of the upper mantle and the crust