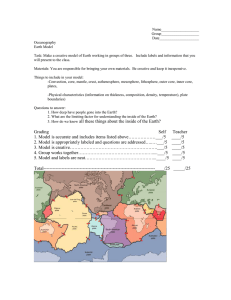
Continental crust
advertisement

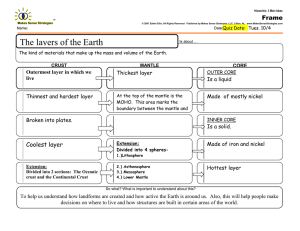
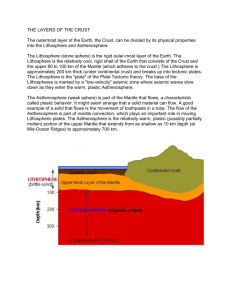
Nebular hypothesis A model of the solar system formation in which a nebula contracts under the force of gravity, eventually flattening into a spinning disk with a central bulge. A protostar forms at the nebula's center. As matter condenses around the protostar in the bulge, planets are formed from the spinning matter in the disk. Inner core Innermost layer of the Earth. Solid made of iron and nickel. Hottest layer. Outer core Layer above the inner core. Liquid made of iron and nickel. Mantle Thickest layer of the earth that sits on top of the outer core. Made of silicate rocksiron, magnesium and silicon. Solid with liquid properties. Crust Outermost layer of the Earth where we live. Made up of light rock, basalt and granite. Continental crust is less dense and thicker than oceanic crust. Lithosphere The crust and uppermost portion of the mantle. Rigid material. Asthenosphere Thin, Slushlike level of the mantle. The lithosphere floats upon the asthenosphere. How old is the Earth according to scientists? 4.6 billion years old How much of earth’s surface is dry land versus Oceans? 29% dry land 71% oceans Three sources of heat for earth’s interior. Meteorite impacts Weight of overlying materials Decay of radioactive isotopes