Plate Tectonics Study Guide
advertisement

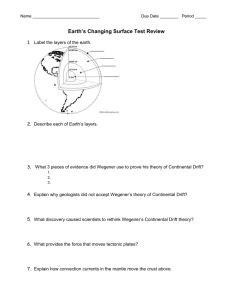
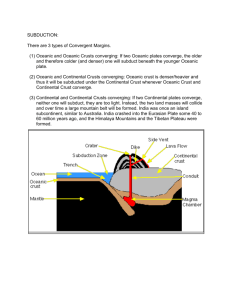
Plate Tectonics Study Guide Name_________________________________________________________Class___________ 1. What does Wegner’s hypothesis of continental drift say? 2. Heat transfer within a fluid takes place by _______________________________. 3. Earth’s inner core is a dense ball of _______________________ metal. 4. How do geologists obtain indirect evidence about Earth’s interior? 5. When the heat source is removed from a fluid, what happens to the convection currents? 6. When you touch a hot pan, energy moves from the pot to your hand. What is this called? 7. Starting with the surface, name the Earth’s layers in order (4 major ones). 8. Where does direct evidence about the Earth’s interior come from? 9. What is Pangaea? 10. What is a transform boundary? 11. What are the three types of evidence Wegener used to support his continental drift hypothesis? 12. State the theory of plate tectonics. 13. Why was Wegener’s idea of continental drift rejected? 14. Why is old oceanic crust more dense than new oceanic crust? 15. What did scientists use in the 1900’s to map the ocean floor? 16. What is subduction? 17. In sea floor spreading, where does molten material rise and erupt from? 18. Where does a rift valley form? 19. What is a convergent boundary? 20. The Earth’s mantle is a layer of ________________________________________. 21. Where are mid-ocean ridges found? 22. Where do scientists think convection currents flow in the Earth? 23. Earth’s magnetic field results from movements in the __________________________. 24. Mountain ranges are a result of______________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________. 25. Oceanic crust near the mid-ocean ridge is _________________ than oceanic crust further away from the ridge. 26. The transfer of heat by the movement of heated fluid is called ____________________. 27. Alfred Wegener provided evidence from landforms, fossils and climate in support of his theory of_____________________________________________. 28. The outermost layer of the Earth is called the ___________________. 29. Along a ___________________________________, two plates slip past each other, moving in opposite directions. 30. If subduction occurs faster than oceanic crust can be created, an ocean will_______________________. 31. Mantle material rises in convection currents because heated materials become _______________ dense. 32. A continental plate collides with an oceanic plate at a _______________________ boundary. 33. When continental plates pull apart as a divergent boundary on land, a __________________________ forms. 34. The lithosphere is broken into sections called ________________________, which float on top of the asthenosphere. 35. The part of the mantel called the _____________________________ is made of soft rock that bends like plastic. 36. Subduction occurs where oceanic crust bends down toward the mantle at a ______________________. 37. Earthquakes produce ________________________ that travel through the Earth. 38. __________________________ is a rock with a fine, dark texture that makes up the oceanic crust. 39. What is a transform boundary? 40. What is sea floor spreading? 41. Energy from the sun that warms your face is transferred by a process called ______________________. 42. That asthenosphere is part of which layer of Earth? 43. Which layer of Earth is made up partly of crust and partly of mantle? 44. Pressure increases with depth toward the center of the Earth. In which layer would you expect pressure to be the greatest? 45. Earth’s solid inner core is surrounded by the hot, molten metal of which layer? 46. What geological features are associated with divergent boundaries? 47. What geological features are associated with convergent boundaries? 48. Describe how the shapes of present day continents support the theory of continental drift. 49. Compare and contrast the outer and inner core.