Chapter 4 Study Guide
advertisement
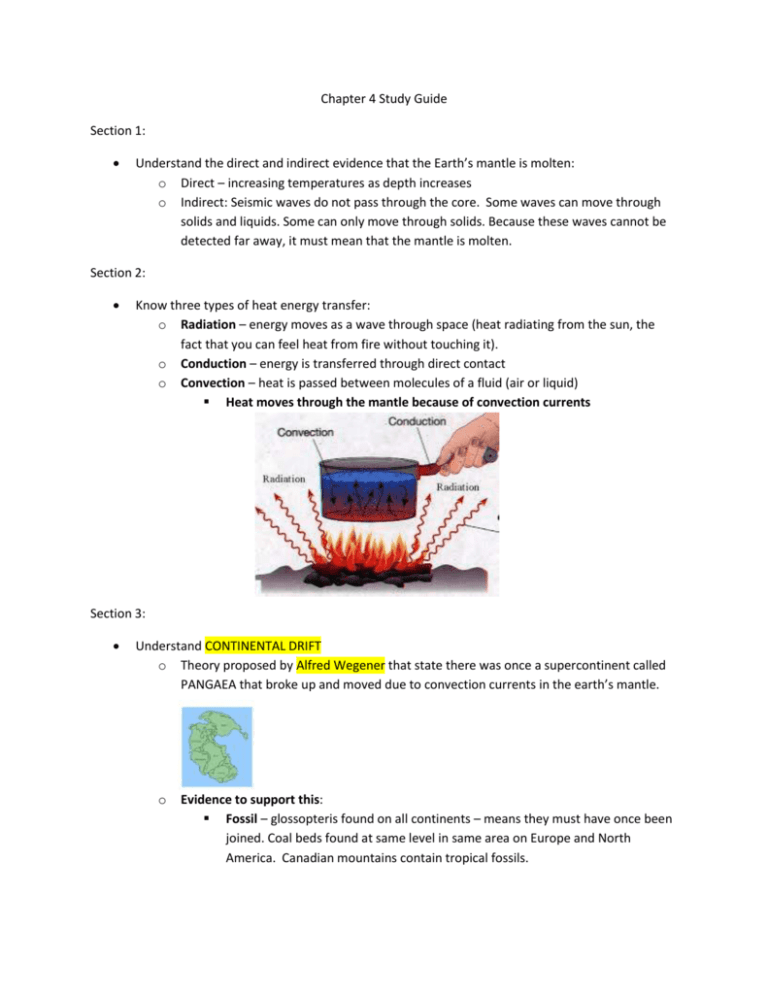
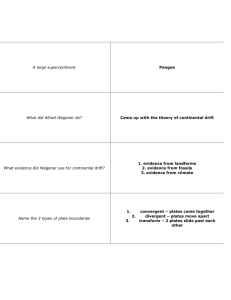
Chapter 4 Study Guide Section 1: Understand the direct and indirect evidence that the Earth’s mantle is molten: o Direct – increasing temperatures as depth increases o Indirect: Seismic waves do not pass through the core. Some waves can move through solids and liquids. Some can only move through solids. Because these waves cannot be detected far away, it must mean that the mantle is molten. Section 2: Know three types of heat energy transfer: o Radiation – energy moves as a wave through space (heat radiating from the sun, the fact that you can feel heat from fire without touching it). o Conduction – energy is transferred through direct contact o Convection – heat is passed between molecules of a fluid (air or liquid) Heat moves through the mantle because of convection currents Section 3: Understand CONTINENTAL DRIFT o Theory proposed by Alfred Wegener that state there was once a supercontinent called PANGAEA that broke up and moved due to convection currents in the earth’s mantle. o Evidence to support this: Fossil – glossopteris found on all continents – means they must have once been joined. Coal beds found at same level in same area on Europe and North America. Canadian mountains contain tropical fossils. Landform – mountain ranges line up along coasts. South America and Africa fit like puzzle pieces Climate – South Africa has geology that shows glaciers once existed there. Spitsbergen in Arctic Circle has tropical fossils. Section 4: Sea – Floor spreading o Sonar used during WWII showed largest mountain chains in the world exist in middle of Atlantic Ocean and stretch to all oceans (Iceland is actually top of ridge) o Ocean floors move like conveyor belts from Mid-Atlantic ridge towards the continents – pushing them apart o Subduction occurs where oceanic crust meets continental crust. Oceanic crust is more dense and slides under continental crust. It eventually melts as it reaches the mantle and is recycled in the convection currents. Evidence for this: o “pillow rocks” look like toothpaste squeezed from tube – can only form when lava cools rapidly under pressure (from ocean) o Magnetic strips in crust – molecules line up facing north and south pole in alternating patterns – means that the earth’s crust is constantly forming throughout history and moving o Drilling – oldest rocks on ocean crust are near the coasts, meaning that it moved. If the crust did not move, all rocks would be same age. Section 5: Plate Tectonics o Juzo Wilson – describes earth’s crust as large plates pushing and pulling on each other Plates touch at FAULTS – where most earthquakes occur Know the types of plate boundaries and forces involved in each: o Transform boundaries(shearing): Divergent Boundaries(tension): Convergent Boundaries(compression):