protein webquest
advertisement
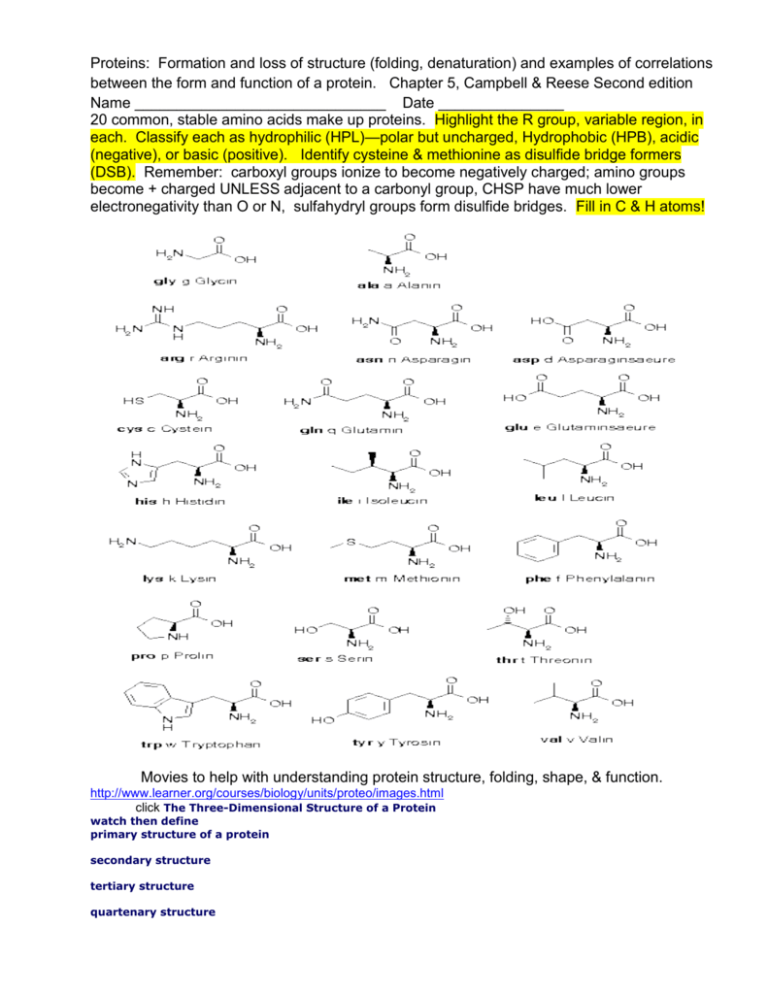
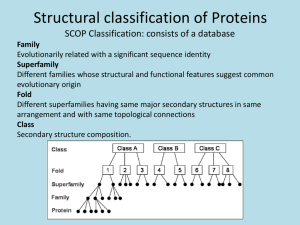
Proteins: Formation and loss of structure (folding, denaturation) and examples of correlations between the form and function of a protein. Chapter 5, Campbell & Reese Second edition Name ______________________________ Date _______________ 20 common, stable amino acids make up proteins. Highlight the R group, variable region, in each. Classify each as hydrophilic (HPL)—polar but uncharged, Hydrophobic (HPB), acidic (negative), or basic (positive). Identify cysteine & methionine as disulfide bridge formers (DSB). Remember: carboxyl groups ionize to become negatively charged; amino groups become + charged UNLESS adjacent to a carbonyl group, CHSP have much lower electronegativity than O or N, sulfahydryl groups form disulfide bridges. Fill in C & H atoms! Movies to help with understanding protein structure, folding, shape, & function. http://www.learner.org/courses/biology/units/proteo/images.html click The Three-Dimensional Structure of a Protein watch then define primary structure of a protein secondary structure tertiary structure quartenary structure http://www.learner.org/vod/vod_window.html?pid=815 protein folding and functions We’ve seen the first half of this movie in class (up to the start of tertiary structure)—watch if you need more help with how proteins attain their functional shape http://www.learner.org/vod/vod_window.html?pid=816 This movie explains the relationship between genetic code and protein structure and function Watch first 12 minutes to better understand protein structure, then move to minute 21--22 to understand how mutation results in sickle cell anemia. http://www.learner.org/resources/series187.html?pop=yes&pid=2036 This movie explains the relationship between a protein’s shape and its role. It introduces the ways that scientists use info on proteins to control traits or develop drugs/therapies. Go to the Campbell place. Click on edition 7. Log in as: Mayfieldstudent1 Password scienceaccount2009 Go to chapter 5. Watch and interact with activity 5.4 protein function. Type of proteins function function Activity 5.4 Protein structure Why are proteins called polypeptides? What happens during formation of primary structure? correlation between structure and What part of primary structure is the same for all proteins? What part of primary structure varies, and how is this variance controlled? How many amino acids are commonly found in proteins? What parts of a protein interact during protein folding? Why? How is an alpha helix different from a Beta pleated sheet? Biologically, why are these differences important (from Annenberg, learner.org world of chemistry proteins: structure and function) What parts of amino acids interact to allow formation of tertiary structure? What three types of interactions are most important? Describe them. How are tertiary and quarternary structures similar? Different? http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=AP13304 Summary of protein folding http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/protein_folding/protein_folding.ht m How do proteins develop their final shape? 1st: 2nd: 3rd: 4th: This animation provides an overview of how proteins attain the correct shape, as well as of how the shape can be distorted during denaturation. http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072943696/student_view0/chapter2/animation__protein_denaturation.html 1. Initially, why does heating a protein cause it to lose its shape? What kinds of bonds are broken? 2. Why doesn’t the protein return to its native shape after heat is removed? 3. Why do denatured proteins , like cooked egg whites, clump up or coagulate? http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/proteinstructure.html Add any new understanding to your comments above. Take the postquiz! http://intro.bio.umb.edu/111F98Lect/folding.html 4. What level of folding is being illustrated? _______________________ What event seems to have a particularly strong impact? _______________________________________________________________________ http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/proteins/hydrophobic%20force.swf what does this animation show? Watch this animation to review: http://www.johnkyrk.com/aminoacid.html How do amino acids differ? How is the difference between a peptide bond and the single covalent bond that links on R groups important in protein folding?