Overview
advertisement

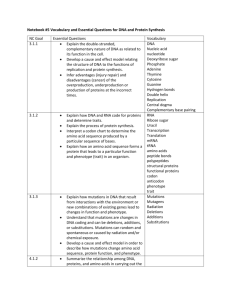
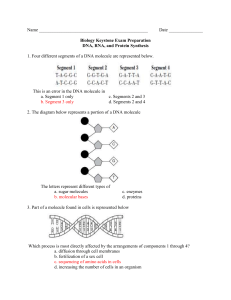
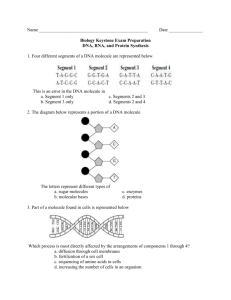
Toobers Overview Students will use the 3-D molecular modeling kits to explore different aspects of the structures of proteins and DNA. Once they have an understanding of the structures, they will look at how these two molecules are related by building a specific protein with a given DNA sequence. Protein folding, Part 1 (Primary to Tertiary structure): Students begin by looking at the side chains of the amino acids. They sort all of the amino acids according to their properties (acidic, basic, hydrophobic, etc..). Then, they randomly place 15 amino acids along the Toober to represent a hypothetical primary structure of the protein. They try to fold the protein to meet different chemical properties, such as all of the hydrophobic side chains need to be buried on the inside to minimize interactions with the polar water molecules. As they continue, they bend the Toober to meet attempt to meet all of the different requirements. Students may be required to change the position of the amino acids to meet all of the requirements. Through this investigation, students see how the sequence of amino acids directs the protein folding via side chain interactions. Protein folding, Part 2(Primary to Secondary to Tertiary structure): This time students build an actual protein to model secondary structures commonly found in proteins. Students follow the instructions to build the protein. The focus this time is how the secondary structures further stabilize the proteins. DNA models: Students investigate the structure of DNA using the information that was available to Watson and Crick. Using smaller pieces they work together to determine the correct overall structure. Through this investigation, students are prompted to look at the different components and how they contribute to the overall stability. Building a protein with a given DNA structure: The goal of this activity is to make the connection between the genetic information held in DNA and the functionality of proteins. Students use a given DNA sequence to transcribe and then translate it into an amino acid sequence. They build the amino acid sequence using the Toober models and fold it to meet the chemical requirements. Then, different types of mutations (point, frame shift, etc.) are introduced, and their effects are observed on the various proteins.