1. Presence of a Nucleus Bacteria
advertisement

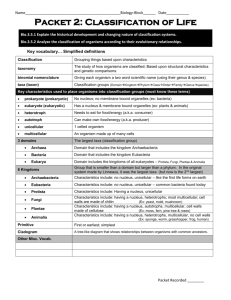
SEC. 18-1 CLASSIFICATION Taxonomy = ____naming_______ of organisms Makes studying the unity & diversity of living things EASIER In binomial nomenclature, each species is assigned a two-part scientific name. The scientific name is always written in italics. The first word is capitalized, and the second word is lowercase The 6 Kingdom System is Based on the Following Criteria: 1. Presence of a Nucleus Bacteria: -DNA not in nucleus – Bacteria two kingdoms called ___prokaryotes___ Other Kingdoms: -DNA in nucleus 2. Number of Cells Unicellular: called Eukaryotes Organism consists of one cell. Multicellular: more than one cell 3. How it Obtains Food Autotroph: •Organism makes its own food. •Photosynthesis •ex: Grass, flower Heterotroph: •Organism CANNOT make its own food. •Hunts or eats for its food. •Ex: Ant, Human Mrs. Goux’s Living Environment /Biology COPY & RETURN TO MRS. GOUX Eubacteria •Unicellular •No Nucleus •Bacteria that we encounter every day •Heterotroph & Autotroph • Archeabacteria Unicellular •No Nucleus • Heterotroph & Autotroph Protists Fungi Plants Animals Ancient bacteria Often live in extreme environments like acidic(low pH), high temperatures and salts •Unicellular •Euglena •Have a nucleus •Ameba •Heterotroph & Autotroph •Paramecium •Uni and Multicellular •Have a nucleus •Have a cell wall •Heterotroph •Break down organic material •Do not move •Multicellular •Have a nuclues •Cell wall •Autotrophic •Yeast •Mushroom •Molds •Trees •Corn •Grass •Largest Kingdom •Worm •Multicellular •Spider •Have nuclues •Penguin •No Cell wall •Whale •Heterotrophic •Invertebrates vs. Vertebrates Mrs. Goux’s Living Environment /Biology COPY & RETURN TO MRS. GOUX Classification Categories From broad groupings Narrow & specific groupings (GENERAL) (SPECIFIC) Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species Every species belongs to ONE of each groupings!!! Complex Kingdom Phylum Class Over Family Genus species Simple Mrs. Goux’s Living Environment /Biology COPY & RETURN TO MRS. GOUX THE 6 KINGDOMS PROKAYOTES Prokaryotes – lack __nuclear____ membranes & most ___organelles_ (= internal membrane-bound structures); without nucleus Eukaryotes – contain ___nuclear____ membranes & organelles 1.) ARCHAEBACTERIA- extreme ancient bacteria that live in __extreme__ environments such as high temperature above boiling, acidic environment (low pH) or highly saline(salt) environment 2.) EUBACTERIA = regular bacteria & blue-green algae --- Cell walls, ____unicellular______ (one cell) Bacteria – _____heterotrophs______ (cannot make own food) Blue-green algae – __autotrophs___ (can make own food) 3) PROTISTA – mostly unicellular a) Protozoa – _animal _-like movement & nutrition Ex. Amoeba & paramecium b) Algae – can form colonies, do photosynthesis, have cell walls, ___plantlike_ __nutrition Ex. Spirogyra, kelp, diatoms, seaweed EUKARYOTES 4.) FUNGI – mostly __multicellular_______ (many cells) --- ____feed______ on other living things Heterotrophs __decomposers_____ of other organisms Cell wall (made of _cellulose____) Ex. Yeasts, molds, mushrooms 5.) PLANTAE (Plants) – mostly multicellular Autotrophs = photosynthetic organisms (can make own food using energy from _sun_____) Cell wall (made of __cellulose______) Ex. Roses, oak & maple trees, cactus, dandelions 6.) ANIMALIA (Animals) – multicellular Heterotrophs _sexual_______ reproduction is very common a) Invertebrates – sponges, worms, insects Have NO __spinal column __ b) Vertebrates – fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, birds Mrs. Goux’s Living Environment /Biology COPY & RETURN TO MRS. GOUX Key Organisms (in order of increasing complexity): Amoeba – has ___psuedopods________ (false feet) for food absorption & movement Paramecium – has __cillia________ for movement & an ____oral groove___(side pocket) through which food is ingested Hydra --- __Two_ cell layers thick --- Has a mouth surrounded by __tentacles_ leading to an internal cavity Earthworm --- _closed__ circulation and tube-like digestion Grasshopper --- _closed____ circulation and tube-like digestion Humans --- Mammals nourish young with __milk_______, have hair/fur & have well-developed brains Dichotomous Key – “di” = __2___; Ex. bicycle, car, jet & motorcycle 1a 1b Requires petroleum fuel Requires only muscle power go to Step 2 __bicycle_______ 2a 2b Has wings and flies Has no wings and does not fly __jet___________ go to Step 3 3a 3b Has two wheels Has more than two wheels __motorcycle ____ ___car__________ Mrs. Goux’s Living Environment /Biology COPY & RETURN TO MRS. GOUX