Packet 12: Introduction to Genetics
advertisement

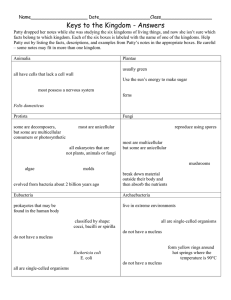
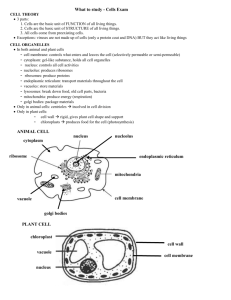
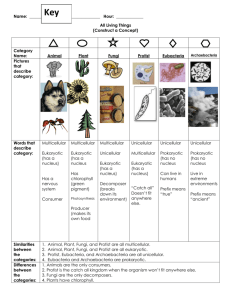
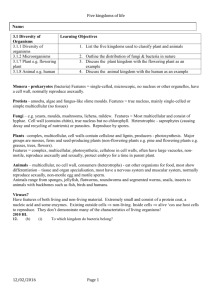
Name______________________________________________Biology-Block______ Date___________ Packet 2: Classification of Life Bio.3.5.1 Explain the historical development and changing nature of classification systems. Bio.3.5.2 Analyze the classification of organisms according to their evolutionary relationships. Key vocabulary… Simplified definitions Classification Grouping things based upon characteristics taxonomy The study of how organisms are classified; Based upon structural characteristics and genetic comparisons. binomial nomenclature Giving each organism a two word scientific name (using their genus & species) taxa (taxon) Classification groups (DomainKingdomPhylumClassOrderFamilyGenusspecies) Key characteristics used to place organisms into classification groups (must know these terms) prokaryote (prokaryotic) No nucleus; no membrane bound organelles (ex: bacteria) eukaryote (eukaryotic) Has a nucleus & membrane bound organelles (ex: plants & animals) heterotroph Needs to eat for food/energy (a.k.a. consumer) autotroph Can make own food/energy (a.k.a. producer) unicellular 1 celled organism multicellular An organism made up of many cells 3 domains The largest taxa (classification group) Archaea Domain that includes the kingdom Archaebacteria Bacteria Domain that includes the kingdom Eubacteria Eukarya Domain includes the kingdoms of all eukaryotes – Protista, Fungi, Plantae & Animalia 6 Kingdoms Group that is smaller than a domain but larger than a phylum. In the original system made by Linneaus, it was the largest taxa (but now is the 2 nd largest) Archaebacteria Characteristics include: no nucleus, unicellular – like the first life forms on earth Eubacteria Characteristics include: no nucleus, unicellular – common bacteria found today Protista Characteristics include: Having a nucleus, unicellular Fungi Plantae Animalia Characteristics include: having a nucleus, heterotrophs; most multicellular; cell walls are made of chitin (Ex: yeast, mold, mushroom) Characteristics include: having a nucleus, autotrophs, multicellular, cell walls made of cellulose (Ex: moss, fern, pine tree & roses) Characteristics include: having a nucleus, heterotrophs, multicellular, no cell walls (Ex: sponge, worm, grasshopper, frog, human) Primitive First or earliest; simplest Cladogram A tree-like diagram that shows relationships between organisms with common ancestors. Other Misc. Vocab. Packet Recorded ________