File
advertisement

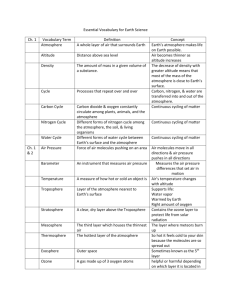
Name: ______________________________________________ Date: 10/15/15 Period: ________ NOTES The Atmosphere Chapter 1.1 and 1.2 What is the atmosphere? What is the atmosphere’s job? What is altitude? What is density? What is the relationship between altitude and density? Where is most of the atmosphere found? Besides gases, what else is found in the atmosphere? What gases make up the atmosphere? Summarize the water cycle. List three sudden events that can cause changes to the atmosphere. Where does most energy come from? What happens to the sunlight that reaches the earth’s surface? What is radiation? What happens when certain gases in the atmosphere absorb infrared radiation (IR)? What is conduction? What is convection? In the atmosphere what direction is the usual motion of convection? What produces the motion of air convection? What causes changes in density of air at the same altitude? (A19) The whole layer of air around the Earth. 1. Keep the earth warm 2. Transport energy around the planet 3. Support & Protect Life Altitude: Distance above sea level Density: amount of mass in a certain amount of volume o Ex: Bowling Ball vs. Soccer ball – they’re about the same size (volume), but are they the same weight (mass)? _________________________________________ Which one has the greater density? __________________ As the altitude in the atmosphere goes up (meaning you get higher above Earth’s surface), the density of the air decreases (becomes less dense). Ex: there’s less air on top of a mountain than at the beach! The lower the density of the air, the harder is for organisms to survive (it’s harder to breathe!) 99.9% is found in the lowest 30 km or 20 miles closest to the Earth’s surface. Solids and liquids such as dust, sea salt, water droplets In Dry Air o 78% Nitrogen o 21% Oxygen o 1% argon, carbon dioxide & other gases 0-4% water vapor – this number can vary (change) Different forms of water go back and forth between the Earth’s surface and the Atmosphere through evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. 1. Volcanic Eruptions: gases and ash enter atmosphere – can affect the air and lower temperatures worldwide (blocks out sunlight!) 2. Forest Fires: adds carbon dioxide to the air as well as ash. 3. Dust Storms: add lots of particles to the air for a while Almost all of the energy around you comes from THE SUN!!! Reflected (bounces off) back into atmosphere OR Absorbed (soaked into) Earth’s surface. Energy that travels across distances in the form of waves Examples: visible light, infrared radiation, and ultraviolet radiation It warms the air (keeps the Earth warmer, slows down cooling) Transfer of energy from one substance to another by direct contact. Examples: o The hot pot handle makes your hand hot o Your feet get hot when you walk barefoot on hot sand Transfer of energy from place to place by the motion of a gas or liquid Example: warmed air rises up and carries heat to the cat on the shelf Up and down Warm air carries the energy up in the atmosphere When the air cools off, it sinks back to the ground Differences in density of the air Changes in temperature Warm air rises and cool air sinks Warm air expands and has fewer particles per cubic inch than cool air What causes the air temperature to change with altitude? What criteria do scientists use to define the 4 layers of the atmosphere. This makes warm air less dense than cool air Different parts of the atmosphere absorb and move energy in different ways Patterns of temperature change in the atmosphere LAYERS OF THE ATMOSPHERE CHART EXOSPHERE / OUTER SPACE IS HERE LAYER Thermosphere 90 km or 56 mi above Earth Details Farthest from Earth’s surface Atmosphere grows less and less dense until it becomes outer space Air is hot because it absorbs solar radiation Auroras occur here Mesosphere 50-90 km or 31-56 mi above Earth Below Thermosphere Air is very thin – very few molecules of air Most meteors burn up here Heated from below by the stratosphere so the temperature goes down as you up go up in altitude Stratosphere 10-50 km or 6-31 mi above Earth Troposphere 0-10 km or 0-6 mi above Earth Below Mesosphere Above troposphere Ozone layer found here Absorbs solar radiation so the temperature increases as you go up in altitude Nearest layer to the Earth – where you live Warmed by the ground so the temperature goes down as you go up in altitude Contains 80% of the atmosphere’s mass Includes all the water vapor Most weather happens here Jet Streams found at top of this layer. EARTH’S SURFACE IS HERE Summary Questions: 1. What gas makes up most of the atmosphere? _____________________________ 2. Why is altitude important when discussing air density? 3. Explain air convection and why it happens. 4. List the 4 layers of the atmosphere in order from closest to Earth’s surface to farthest.